- #1
rwooduk
- 762
- 59
- TL;DR Summary
- I am looking for advice on statistical analysis of a PMT signal
Hello,
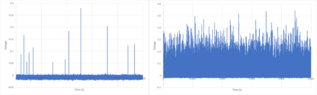
I have recently started collecting photomultiplier tube (PMT) tube data, and I'm curious how best to analyse it (attached right). I also have a background capture (attached left). I am looking to get the relative total intensity and any other statistical analysis I could make. Is anyone familiar with such a signal?
Thanks for any advice.
I have recently started collecting photomultiplier tube (PMT) tube data, and I'm curious how best to analyse it (attached right). I also have a background capture (attached left). I am looking to get the relative total intensity and any other statistical analysis I could make. Is anyone familiar with such a signal?
Thanks for any advice.