SUMMARY
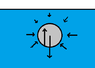
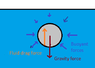
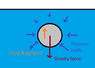
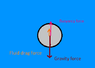
The discussion focuses on the forces acting on a stone sinking in water, specifically addressing buoyant force, fluid drag force, and gravitational force. It is established that both buoyant force and fluid drag act upwards while gravity acts downwards. When the stone reaches terminal velocity, the net vertical force is zero, leading to the equation Fgravity + Fbuoyancy + Fdrag = 0. The true buoyant force is defined as the vector sum of pressure loads, and the relationship between buoyant force and fluid drag varies depending on the object's density.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Newton's laws of motion
- Familiarity with fluid dynamics concepts
- Knowledge of Free Body Diagrams (FBD)
- Basic principles of buoyancy and density
NEXT STEPS
- Study the principles of buoyancy and Archimedes' principle
- Learn about fluid drag force and its dependence on object shape and velocity
- Explore the concept of terminal velocity in fluid mechanics
- Investigate the effects of vortex shedding on drag forces
USEFUL FOR
Physics students, educators, and anyone interested in understanding the dynamics of objects submerged in fluids, particularly in relation to buoyancy and drag forces.