SUMMARY
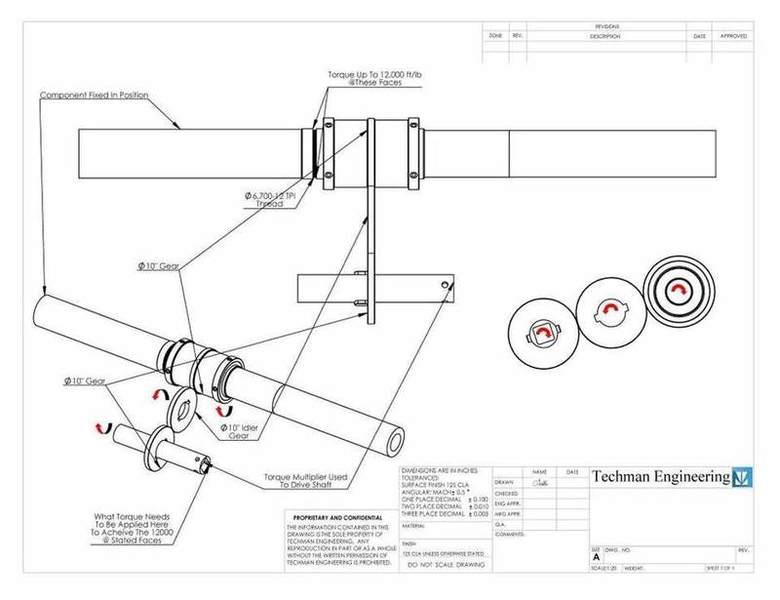
This discussion focuses on calculating torque for a shaft using a torque multiplier with a 125:1 ratio. The key formulae involved are torque = force x distance and power = torque x angular speed. To achieve 12,000 ft-lbs at the output shaft, the input torque must be calculated as 12,000 / 125, resulting in approximately 96 ft-lbs. The torque multiplier operates through an enclosed arrangement of gears, allowing for precise torque application via a torque wrench.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of torque and force calculations
- Familiarity with gear ratios and mechanical advantage
- Knowledge of torque multipliers and their function
- Basic principles of angular speed and power in mechanical systems
NEXT STEPS
- Research "Torque Multiplier Calculations" for practical applications
- Learn about "Mechanical Advantage in Gear Systems" to understand force amplification
- Study "Torque Wrench Calibration" for accurate torque application
- Explore "Angular Speed and Power Relationships" in mechanical engineering
USEFUL FOR
Mechanical engineers, technicians working with torque applications, and anyone involved in machinery maintenance or design will benefit from this discussion.
 [/PLAIN]
[/PLAIN]