MatusVeselka
- 2
- 0
Homework Statement
Hello I am trying to predict vector after collision of 2 ball in biliard. I am using angle-free representation formulas from wikipedia : https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/14d5feb68844edae9e31c9cb4a2197ee922e409cx1 and x2 are positions of balls, m1 and m2 are masses of balls, v1 and v2 are vectors of direction before collision and the angle brackets indicate the inner product (or dot product) of two vectors.
my values are :
x1 = (0.5 , 0)
x2 = (0 , 1)
m1,m2 = 1
v1 = (0.5, 1)
v2 = (0, 0)
Homework Equations
The Attempt at a Solution
[/B]
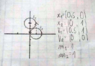
And here its my solution with vector (0.835 , 0.329), but this result can't be correct can somebody help me what I am doing wrong ? My result is total wrong and i don't know why