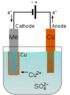Electrolysis of Water: How Does the Electric Field Affect Covalent Bonds?
- Context: Undergrad
- Thread starter erocored
- Start date
-
- Tags
- Electrolysis Work
Click For Summary
The discussion centers on the electrolysis of water and the behavior of CuSO₄ in an electrolytic cell. Participants clarify that CuSO₄ dissociates into Cu²⁺ and SO₄²⁻ ions when dissolved in water, facilitated by the stabilization provided by water molecules. The right electrode becomes positively charged due to the loss of electrons when Cu atoms dissolve into Cu²⁺ ions, while the left electrode attracts these ions, leading to their deposition. The conversation also highlights that while the electric field influences ion movement, it does not directly break covalent bonds in water; rather, it facilitates the migration of ions and the electrochemical reactions involved in water electrolysis.
PREREQUISITES- Understanding of electrolysis and electrolytic cells
- Familiarity with ionic dissociation in aqueous solutions
- Knowledge of the behavior of electrodes in electrochemical reactions
- Basic principles of molecular orbital theory and energy levels
- Study the electrolysis of water and the associated half-reactions
- Learn about the Grotthuss mechanism in proton migration
- Explore the role of electrolytes in enhancing electrolysis efficiency
- Investigate the principles of ionic dissociation and solvation in aqueous solutions
Chemistry students, electrochemists, and anyone interested in understanding the principles of electrolysis and the behavior of ionic compounds in solution.
Similar threads
- · Replies 5 ·
- · Replies 3 ·
- · Replies 8 ·
- · Replies 20 ·
- · Replies 5 ·
- · Replies 3 ·
- · Replies 1 ·
- · Replies 14 ·
- · Replies 4 ·
- · Replies 3 ·