Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around determining the number of distinct necklaces that can be created using $m$ symmetric beads and $k$ colors, utilizing Burnside's Formula. Participants explore the implications of rotations and reflections on the configurations of necklaces, as well as the mathematical underpinnings of the dihedral group associated with these symmetries.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory
- Mathematical reasoning
- Conceptual clarification
- Debate/contested
Main Points Raised
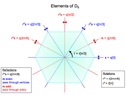
- Some participants propose that the group $G$ is the dihedral group $D_m$, which accounts for the symmetries of the necklace through rotations and reflections.
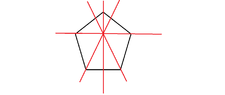
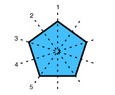
- There is a discussion about how many configurations remain unchanged under specific rotations, with examples provided using $m=4$ and $m=5$ beads.
- Participants question how to determine the number of elements that leave a configuration unchanged under various rotations.
- Some participants suggest that necklaces with all beads of the same color remain unchanged under a rotation by one bead, leading to a count of $k$ such necklaces.
- Others argue that necklaces with alternating colors can remain unchanged under a rotation by two beads, leading to a count of $k^2$ such necklaces.
- There is uncertainty about how to generalize these findings for different values of $m$ and the implications for the number of unchanged configurations under various rotations.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express differing views on the implications of rotations and reflections, with no consensus reached on the general method for counting unchanged configurations. The discussion remains unresolved regarding the specific counts for different arrangements and the generalization of these concepts.
Contextual Notes
Limitations include the need for further clarification on the assumptions regarding the arrangements of beads and the definitions of the groups involved. The discussion also highlights unresolved mathematical steps in applying Burnside's Formula to this specific problem.