SUMMARY
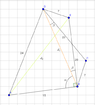
The discussion focuses on calculating the area of quadrilateral ABCD with given side lengths of AB = 15, AD = 24, BC = 7, CD = 20, and the angles ABD and BDC summing to 90 degrees. The suggested approach involves applying the formula for the area of a quadrilateral when two opposite angles are right angles. The solution emphasizes the importance of understanding the relationship between the side lengths and angles in determining the area accurately.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of basic geometry concepts, particularly quadrilaterals.
- Familiarity with the properties of angles and their relationships in polygons.
- Knowledge of area calculation formulas for quadrilaterals.
- Ability to apply trigonometric principles in geometric contexts.
NEXT STEPS
- Research the formula for the area of a quadrilateral given two sides and the included angle.
- Explore the application of the Law of Cosines in quadrilateral area calculations.
- Learn about the Brahmagupta's formula for cyclic quadrilaterals.
- Study the relationship between angles and side lengths in irregular polygons.
USEFUL FOR
Students studying geometry, educators teaching quadrilateral properties, and anyone interested in advanced area calculations for polygons.