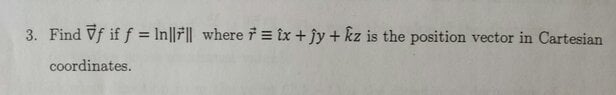Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around finding the gradient of the function \( f = \ln |r| \), where \( r \) is defined in terms of Cartesian coordinates \( (x, y, z) \). Participants explore various approaches to compute the gradient, including the use of the chain rule and partial derivatives. The conversation includes attempts at mathematical derivations and clarifications of notation.
Discussion Character
- Technical explanation
- Mathematical reasoning
- Debate/contested
Main Points Raised
- Some participants suggest starting the gradient calculation by differentiating each component of the vector \( r \) individually.
- One participant attempts to derive the gradient and proposes that it simplifies to \( \frac{\mathbf{r}}{r^2} \), but questions whether this is correct.
- Another participant points out the need to use the chain rule for the gradient and expresses confusion over the notation used in earlier posts.
- There are attempts to relate the gradient of \( \ln(\| \mathbf{r} \|) \) to the components of \( r \) and to derive the gradient of \( \frac{1}{r} \), leading to different expressions for the gradients.
- Multiple participants provide their interpretations of the gradient calculations, with some deriving \( -\frac{\mathbf{r}}{r^3} \) for the gradient of \( \frac{1}{r} \) and others questioning the correctness of these results.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express differing views on the correct approach to calculating the gradient, with no consensus reached on the final expressions or methods. Some calculations are challenged or questioned, indicating ongoing uncertainty.
Contextual Notes
Participants reference specific mathematical steps and notations that may not be universally understood, leading to confusion. There are also unresolved issues regarding the correctness of various gradient expressions derived during the discussion.