You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
What is Ln: Definition and 183 Discussions
The natural logarithm of a number is its logarithm to the base of the mathematical constant e, where e is an irrational and transcendental number approximately equal to 2.718281828459. The natural logarithm of x is generally written as ln x, loge x, or sometimes, if the base e is implicit, simply log x. Parentheses are sometimes added for clarity, giving ln(x), loge(x), or log(x). This is done particularly when the argument to the logarithm is not a single symbol, so as to prevent ambiguity.
The natural logarithm of x is the power to which e would have to be raised to equal x. For example, ln 7.5 is 2.0149..., because e2.0149... = 7.5. The natural logarithm of e itself, ln e, is 1, because e1 = e, while the natural logarithm of 1 is 0, since e0 = 1.
The natural logarithm can be defined for any positive real number a as the area under the curve y = 1/x from 1 to a (with the area being negative when 0 < a < 1). The simplicity of this definition, which is matched in many other formulas involving the natural logarithm, leads to the term "natural". The definition of the natural logarithm can then be extended to give logarithm values for negative numbers and for all non-zero complex numbers, although this leads to a multi-valued function: see Complex logarithm for more.
The natural logarithm function, if considered as a real-valued function of a real variable, is the inverse function of the exponential function, leading to the identities:
e
ln
x
=
x
if
x
>
0
,
ln
e
x
=
x
.
{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}e^{\ln x}&=x\qquad {\text{if }}x>0,\\\ln e^{x}&=x.\end{aligned}}}
Like all logarithms, the natural logarithm maps multiplication of positive numbers into addition:
ln
x
y
=
ln
x
+
ln
y
.
{\displaystyle \ln xy=\ln x+\ln y.}
Logarithms can be defined for any positive base other than 1, not only e. However, logarithms in other bases differ only by a constant multiplier from the natural logarithm, and can be defined in terms of the latter. For instance, the base-2 logarithm (also called the binary logarithm) is equal to the natural logarithm divided by ln 2, the natural logarithm of 2.
Logarithms are useful for solving equations in which the unknown appears as the exponent of some other quantity. For example, logarithms are used to solve for the half-life, decay constant, or unknown time in exponential decay problems. They are important in many branches of mathematics and scientific disciplines, and are used in finance to solve problems involving compound interest.
View More On Wikipedia.org
The natural logarithm of x is the power to which e would have to be raised to equal x. For example, ln 7.5 is 2.0149..., because e2.0149... = 7.5. The natural logarithm of e itself, ln e, is 1, because e1 = e, while the natural logarithm of 1 is 0, since e0 = 1.
The natural logarithm can be defined for any positive real number a as the area under the curve y = 1/x from 1 to a (with the area being negative when 0 < a < 1). The simplicity of this definition, which is matched in many other formulas involving the natural logarithm, leads to the term "natural". The definition of the natural logarithm can then be extended to give logarithm values for negative numbers and for all non-zero complex numbers, although this leads to a multi-valued function: see Complex logarithm for more.
The natural logarithm function, if considered as a real-valued function of a real variable, is the inverse function of the exponential function, leading to the identities:
e
ln
x
=
x
if
x
>
0
,
ln
e
x
=
x
.
{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}e^{\ln x}&=x\qquad {\text{if }}x>0,\\\ln e^{x}&=x.\end{aligned}}}
Like all logarithms, the natural logarithm maps multiplication of positive numbers into addition:
ln
x
y
=
ln
x
+
ln
y
.
{\displaystyle \ln xy=\ln x+\ln y.}
Logarithms can be defined for any positive base other than 1, not only e. However, logarithms in other bases differ only by a constant multiplier from the natural logarithm, and can be defined in terms of the latter. For instance, the base-2 logarithm (also called the binary logarithm) is equal to the natural logarithm divided by ln 2, the natural logarithm of 2.
Logarithms are useful for solving equations in which the unknown appears as the exponent of some other quantity. For example, logarithms are used to solve for the half-life, decay constant, or unknown time in exponential decay problems. They are important in many branches of mathematics and scientific disciplines, and are used in finance to solve problems involving compound interest.
View More On Wikipedia.org
-
L
How do you prove that ln(a^x) = xln(a) and a^x = e^xln(a) without using exponent rules?
In the book "Calculus by Michael Spivak" it says that a^x = e^xln(a) is a definition. And I am not convinced to accept this as true without a proof.- logicgate
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Exponential Ln Proof
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Calculus and Beyond Homework Help
-
L
What is the derivative of ln(x)^e ?
Can't figure it out, here's a screenshot with better typography.- lIllIlIIIl
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Calculation Derivative Ln
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Calculus and Beyond Homework Help
-
A
Convergence of a series involving ln() terms in the denominator of a fraction
good day I want to study the convergence of this serie and want to check my approch I want to procede by asymptotic comparison artgln n ≈pi/2 n+n ln^2 n ≈n ln^2 n and we know that 1/(n ln^2 n ) converge so the initial serie converge many thanks in advance!- Amaelle
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Convergence Fraction Ln Series Terms
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Calculus and Beyond Homework Help
-

Is this a valid explanation of why ln() is unbounded near zero?
So far, I found the derivative of ##f##: \begin{align*} \frac{d}{dx}\,f(x)&=&-\frac{d}{dx}\,\ln(-x)\\ &=&-\left(\frac{1}{(-x)}\right)(-1)\\ &=&-\frac{1}{x} \end{align*} ##f'(x)## is always positive and never zero on its domain. Hence, ##f## does not have a local maximum and is always...- Eclair_de_XII
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Explanation Ln Zero
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Calculus and Beyond Homework Help
-

MHB 2.2.1 AP Calculus Exam .... derivative with ln
If $f(x)=7x-3+\ln(x),$ then $f'(1)=$ $a.4\quad b. 5\quad c. 6\quad d. 7\quad e. 8$ see if you can solve this before see the proposed solution- karush
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Ap Ap calculus Calculus Derivative Exam Ln
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Calculus
-

MHB 3.4.238 AP calculus exam Limits with ln
238 Solve $$\displaystyle\lim_{h\to 0} \dfrac{\ln{(4+h)}-\ln{h}}{h}$$ $$(A)\,0\quad (B)\, \dfrac{1}{4}\quad (C)\, 1\quad (D)\, e\quad (E)\, DNE$$ The Limit diverges so the Limit Does Not Exist (E)ok the only way I saw that it diverges is by plotting not sure what the rule is that observation... -
E
Relationship between ln k and 1/t using different formula
Hi, I'm currently taking Chemistry 101 and came across this equation that seems to contradict what I've learned before. I don't know the name of it, but here is the equation and its implication. Now another equation we have learned is the Arrhenius equation, which is as follows: If I...- Ethan Cheng
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Chemistry
-

What is the difference quotient of ln (x^3 -5)? Picture provided....
Mentor note: Thread moved from technical math section, so is missing the homework template .[ATTACH=full]234622[/ATTACH]- Michael Santos
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Difference Ln Picture quotient
- Replies: 22
- Forum: Calculus and Beyond Homework Help
-
D
Binary Representation: Log or Ln?
What is the difference between log and ln?? [Thread moved to General Math forum by moderator]- Dominic M Sangma
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Difference Ln Log
- Replies: 5
- Forum: General Math
-

Power Series and Convergence for ln(x+1)
Homework Statement What is the power series for the function ln (x+1)? How do you find the sum of an infinite power series? Homework Equations sigma from n=1 to infinity (-1)^n+1 (1/n2^n) That is the power series, how is that equivalent to ln (x+1)? How do you find the sum, or what does it...- Eric Song
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Ln Power Power series Series
- Replies: 22
- Forum: Calculus and Beyond Homework Help
-
T
MHB Integral of tan^2 ln^2: $\pi/2 (1-\ln 2)$
Show that, $$\int_{0}^{\pi/2}{\ln^2 (\tan^2 \theta)\over \pi^2+\ln^2 (\tan^2 \theta)}\mathrm d\theta=\color{red}{\pi\over 2}\color{green}(1-\ln 2)$$- Tony1
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: General Math
-
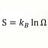
B Clarification : S = K ln W and S = K ln omega
With S = K ln W where W is probability system is in the state it is in relative to all other possible states : W = VN , V = volume, N = number of particles so ln W = N (ln V) And this expression is for non equilibrium state. For equilibrium state S = K ln Ω Then is the only difference between...- morrobay
- Thread
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Classical Physics
-
M
MHB What is the difference between log and ln?
In simple words, what is the difference between log and ln?- mathdad
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Difference Ln Log
- Replies: 3
- Forum: General Math
-
D
When to Use Ln vs Log in Calculating Derivatives?
Homework Statement I'm having a hard time differentiating when to use log instead of ln, vice versa. Are there any general rules to follow? For example I have to evaluate 4u^-3 + u^-1. Homework Equations f'(1/u) = log u f'(1/u) = ln u The Attempt at a Solution I put -2u^-2 + log(u) but the...- Drake M
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Calculus and Beyond Homework Help
-
D
A Integral ##\int_{-1}^{1} [P_{l}^{m}]^2 ln [P_{l}^{m}]^2 dx##
Hi, todos: Do you know how to calculate the definte integral for Integral for ##\int_{-1}^{1} [P_{l}^{m}]^2 \ln [P_{l}^{m}]^2 dx##, where ##P_{l}^{m} (x)## is associated Legendre functions. Thanks for your time and help.- dongsh2
- Thread
- Replies: 12
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-

B Not following an integral solution
In the image below, why is the third line not \frac {ln(cosx)} {sinx}+c ? Wouldn't dividing by sinx be necessary to cancel out the extra -sinx that you get when taking the derivative of ln(cosx)? Also, wouldn't the negatives cancel? -

B Solving SI Units with ln(n): A High School Puzzler
I tried with Google but I couldn't find anything, so here goes: When I "use ln on a quantity" (I don't really know how to phrase it in english, as we just have a verb for it), say, I have n = 0.00149 kg/m*s, and I put it into the ln, so now I have ln(0.00149 kg/m*s) what happens to the SI Units...- Const@ntine
- Thread
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-
C
What is the Domain of ln(x^2 + y^2)?
Homework Statement for the domain of ln (x^2 + y^2 ) , it it given in my notes that the ans is x ≠ 0 and y ≠ 0 IMO , it's wrong to give x ≠ 0 and y ≠ 0 , because the meaning of x ≠ 0 and y ≠ 0 is that x and y can't be 0 all the times so just leave the ans (x^2 + y^2 ) > 0 , will do ...- chetzread
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Calculus and Beyond Homework Help
-
C
Domain of z= ln ( (x^2) + (y^2) )
Homework Statement the given ans is x ≠ 0 , y ≠ 0 , the ans given is x ≠ 0 , y ≠ 0 . I don't understand the ans , why the author leave the ans like this ? IMO , x can be 0 as long as y not = 0 y also can be 0 , as long as x not = 0 ,by giving the ans in x ≠ 0 , y ≠ 0 , the author just rule out...- chetzread
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Calculus and Beyond Homework Help
-
A
Inifinity limit with natural log
Homework Statement Limx--> ∞ Ln(x^2-1) -Ln(2x^2+3) Homework EquationsThe Attempt at a Solution Ln(x^2-1)/(2x^2+3) Then I divided the top and bottom by x^2 so in the end I got (1/2). Is this right?- AlexandraMarie112
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Calculus and Beyond Homework Help
-

MHB 242.q2.3a Int_2^4 dx/[x( ln x)^2]
$\Large{242.Q2.3a} \\ \text{find the integral} \\ \displaystyle \int_2^4 \frac{dx}{x( ln\, x)^2} $ -

MHB How Do You Differentiate a Natural Logarithm Function Like This?
$\large{242.7.3.83}$ Differentiate $$\displaystyle f(x)=\ln\left[{\frac{(2x+3)(x+6)^5}{(1-2x)^3}}\right]$$ Assume first step is expansion.. $$f(x)=\ln\left({2x+3}\right) +5\ln\left({x+6}\right) -3\ln\left({1-2x}\right)$$- karush
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Derivative Ln
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Calculus
-
T
MHB Equality of natural ln function
I have this equality: $$ (\ln\left({n}\right))^4 < {n}^{\frac{1}{4}} $$ where $ n > 1$ Can I derive a law from this such that $$ (\ln\left({n}\right))^b < {n}^{\frac{1}{b}} $$ where $n > 1$ ?- tmt1
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: General Math
-
T
MHB Why Is the Limit of This $\ln$ Sequence Incorrect?
If I have this sequence $$a_n = \ln\left({\frac{n}{n^2 + 1}}\right)$$ I need to find: $$ \lim_{{n}\to{\infty}} \ln\left({\frac{n}{n^2 + 1}}\right)$$ Shouldn't I be able to find the limit of$$ \lim_{{n}\to{\infty}} \frac{n}{n^2 + 1}$$ (which is $0$) and then substitute the result of that... -

Exponential having ln exponent
Homework Statement How is ## e^log√(1-x^2)## equal to ##√(1-x^2)?##Homework EquationsThe Attempt at a Solution taking ln on the function, ln√(1-x^2). lne⇒ ln√(1-x^2) ....- chwala
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Exponent Exponential Ln
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Calculus and Beyond Homework Help
-
I
I Semi ln plot- uncertainty estimation
Hello there! There is a problem with calculating the uncertainty from semi- ln plot. The linear fitting gives standard errors as you can see in attached picture. In the Y axis are ln J values, obviously. If the intersection with y-axis, x=0, then we get the point y=b=-33,21, and it's ln J', so...- Imperatore
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Estimation Ln Plot Uncertainty
- Replies: 4
- Forum: General Math
-

I Ln x as a logarithmic function
My book finds a function of x say ln(x). It is the area under 1/x. Having the properties (d/dx) ln x = 1/x and ln 1 = 0. It says it determines ln(x) completely. It satisfies the laws of logarithms, but why can I regard it as a logarithm just because it satisfies those laws?- ruivocanadense
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Function Ln Logarithmic
- Replies: 17
- Forum: General Math
-
J
I Weinberg LN in QM (Section 3.5): Momentum operator
Hi everyone, Weinberg uses spatial translation invariance to derive the momentum operator. But the way he does it puzzles me. Here is an excerpt of the book. Equation 3.5.1 is the definition of the unitary operator ##U(x)## for translation invariance: $$U^{-1}(x)XU(x) = X+x,$$ with... -
G
Limit of arccosh x - ln x as x -> infinity
Homework Statement find the limit of arccoshx - ln x as x -> infinity Homework Equations ##arccosh x = \ln (x +\sqrt[]{x^2-1} )## The Attempt at a Solution ## \lim_{x \to \infty }(\ln (x + \sqrt{x^2-1} ) - \ln (x)) = \lim_{x \to \infty} \ln (\frac{x+\sqrt{x^2-1}}{x}) \ln (1 + \lim_{x \to...- GwtBc
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Calculus and Beyond Homework Help
-

2(5) − cot [4 arctan 0.2 + (i/2) ln i] − 1
Don't ever divide anything by the quantity in the title. Post your favorite "fancy zeros" here.- Jenab2
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Ln
- Replies: 10
- Forum: General Math
-
M
Is ln(x) differentiable at negative x-axis
Since lnx is defined for positive x only shouldn't the derivative of lnx be 1/x, where x is positive. My books does not specify that x must be positive, so is lnx differentiable for all x?- Miraj Kayastha
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Calculus
-

Integrating differential equations that have ln
Hey guys, I have a question concerning the rewriting of a differential equation solution. In the example above, they rewrite [y=(plus/minus)e^c*sqrt(x^2+4)] as [y=C*sqrt(x^2+4)]. I understand that the general solution we get as a result represents all the possible functions, but if we were to... -
P
What is the Entropy of a System with Doubly Degenerate Energy Level?
An old book I have on elementary Statistical Mechanics (Rushbrooke) uses as an especially simple case a system with one energy level. This level is doubly degenerate. The author doesn't give an example of such a system. Can anyone think of one? And would it have entropy k\ ln 2? [My thoughts...- Philip Wood
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
K
What Value of x Maximizes the Function y=axln(b/x)?
Homework Statement $$y=a\cdot x\cdot ln\left(\frac{b}{x}\right)$$ The derivative should be 0 (to maximize), what's x? Homework Equations $$(ln\:x)'=\frac{1}{x}$$ $$(x^a)'=ax^{(a-1)}$$ $$(uv)'=u'v+v'u$$ The Attempt at a Solution $$\dot y=a \left[ ln \left( \frac{b}{x} \right)-x\frac{x}{b}x^{-2}...- Karol
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Derivative Ln
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Calculus and Beyond Homework Help
-

MHB Methods for showing divergence of $\sum_{1}^{\infty} ln(1+\frac{1}{n})$?
Does\: $ \sum_{1}^{\infty} ln(1+\frac{1}{n}) $\: converge? I tried the limit comparison test with bn=1/n and got that it diverges, which also looks right. However I also tried the ratio test: $ \lim_{{n}\to{\infty}} \left| \frac{{a}_{n+1}}{{a}_{n}} \right| = \lim_{{n}\to{\infty}} \left|... -
Questions on ln and e^x graphs
Greetings, I have some questions about ln(x) and e^x graphs , with figuring out Domain , range and line of asymptote. Q1) How can I know if this graph is ln(x) or e^x (I thought it was e^x graph since there's no x-axis intercept , however the answer in marking scheme is: Domain : xεR , x>-3...- Samurai44
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Precalculus Mathematics Homework Help
-
M
Solving for x in ln and e equations | Homework Help
Homework Statement I need to solve x: ln (1+e^-x)=-x+2Homework EquationsThe Attempt at a Solution ln (1+e^-x)=-x+2 x+ln (1+1/e^x)=2 x+ln (e^x/e^x+1/e^x)=2 x+ln ((e^x+1)/e^x)=2 x+ln (e^x+1)-ln(e^x)=2 x+ln (e^x+1)-x=2 ln (e^x+1)=2im stuck here. thank you- math007
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Ln
- Replies: 23
- Forum: Precalculus Mathematics Homework Help
-

MHB How to Find the Gradient of ln|r|?
To solve the gradient f when f = ln |r| do I start with differentiating each x,y,z term of the vector?Like ln|x| ln|y|...etc.- Logan Land
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Calculus
-
F
MHB Does e^{2 \ln{|x|}} = |x^2| or x^2?
is e^{2 \ln{|x|}} = |x^2| or x^2?- find_the_fun
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: General Math
-
B
The Difference Between Log and Ln
Both are logarithms, what is the difference between log and ln?- basty
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Difference Ln Log
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Calculus
-
C
Rewriting Ln function and getting a wrong function?
This is really strange: If i rewrite a potens function i get a function which should not be possible (it does not give the same values). What did i do wrong? Y = b*X^a lnY = ln(b*X^a) lny = lnb + ln X^a lnY = lnb + a*lnx we raise both sides to e Y = b+ e^(a*lnx)=b+(...- christian0710
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Precalculus Mathematics Homework Help
-
G
Split ln() of two exponential summands
Homework Statement Dear all I am calibrating a temperature measurement model and I am stuck with an equation. The variable z is given; x and y represent two regression terms with common regressors - which I will solve for a specific regressor in a second step. Homework Equations...- globi
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Exponential Ln Split
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Calculus and Beyond Homework Help
-
A
Determination of order of reaction from ln() graphs
I have to say if each reactant is first, second or zeroth order. Now, I know that usually, we have plots of ln([]) over time. But my teacher wants to trick me. Here is how I do this: Take two data points: convert them to [ ] and normal rate (remove the ln() function). Compare the two...- alingy1
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Determination Graphs Ln Reaction
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Biology and Chemistry Homework Help
-
D
First, second and third deriative of ln (tan x )
Homework Statement y=ln(tan x), dy/dx=2/(sin2x) and d2y/dx2= -4(cos 2x)/(sin 2x)^2 , show that d3y/dx3 = ((4)(3+cos 4x))/(sin 2x)^3 ... i got the solution for dy/dx and d2y/dx2 but not d3y/dx3 , can anyone show me how to get d3y/dx3 please? Thanks in advance! Homework Equations The...- delsoo
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Ln
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Calculus and Beyond Homework Help
-
Y
MHB Solve Integral of ln(x^2-1) with Ease: Step-by-Step Guide
Hello all, I am trying to solve this integral, \[\int \ln(x^{2}-1) \, dx\] but I get stuck no matter what I do, if I go for substitution or parts... thanks- Yankel
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Integration Ln
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Calculus
-

Why is natural log abbreviated as ln and not nl ?
Why is natural log abbreviated as "ln" and not "nl"? I've been taking calculus for a while now and I was just wondering why natural logarithm is abbreviated as "ln" and not "nl". I'm just curious!- sheldonrocks97
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Ln Log Natural Natural log
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Calculus
-

How Do You Calculate the Decay Rate of C14 with a Given Half-Life?
Doing some self prep for Diff EQ starting next week. Determine the decay rate of C14 which has a 1/2 life of 5230. Using e^kt as a function, I solve using k5230=ln.5 which gives the obvious answer of negative what I want. How do I know to use the reciprocal (ln2) other than to "just know" I...- KevinMWHM
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Exponential Ln
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Calculus and Beyond Homework Help
-
9
Ln(9/4) + ln (16/9) - ln (3/1)
Homework Statement If you have, for example, 2 + 4 - 1, you can get the answer (5), by doing both: = 2 + (4 - 1) and, = (2 + 4) - 1 But the same logic does not work with logs: to get the right answer (4/3) here you must do: =(ln(9/4) + ln (16/9)) - ln (3/1) and NOT...- 939
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Ln
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Precalculus Mathematics Homework Help
-
X
Why Does the Taylor Polynomial of Ln(x) Alternate in Sign?
I need help understanding why the ln (x) taylor polynomial is (x-1)-1/2(x-1)^2... + etc. I cannot grasp the concept..- xtrubambinoxpr
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Ln Polynomial Taylor
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Calculus
-
F
MHB Do you need absolute value around argument for log and ln?
When I learned about derivatives I was taught to put the absolute value sign around the argument for ln and log. For example \log{|x|} and \ln{|x|} instead of log(x)ln(x). Does this make a difference? Should both brackets and the straight lines be used? When taking the derivative what is the...- find_the_fun
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Calculus