Discussion Overview
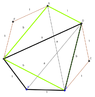
The discussion revolves around proving the equation \((a+b)^2(a-b)=ab^2\) related to the diagonals of a heptagon with equal side lengths. The focus is on the mathematical reasoning and proof techniques involved in this geometric problem.
Discussion Character
Main Points Raised
- One participant presents the problem by defining the side lengths of a heptagon as equal to 1 and specifies the diagonals \(\overline{AD}=a\) and \(\overline{BG}=b\) with the condition \(a>b\).
- Another participant greets the first, indicating a social interaction rather than contributing to the mathematical discussion.
- A subsequent post hints at a potential approach to the proof, although the content of the hint is not provided.
- A later reply indicates an attempt to solve the problem using the hint, but does not detail the method or results of that attempt.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
The discussion does not show clear agreement or disagreement on the proof itself, as the mathematical content is limited and primarily consists of social exchanges and hints.
Contextual Notes
The discussion lacks detailed mathematical steps or assumptions that may be necessary for a complete proof. The hint provided is not elaborated upon, leaving the proof approach ambiguous.
Who May Find This Useful
Participants interested in geometric proofs, particularly those involving polygons and diagonal relationships, may find this discussion relevant.