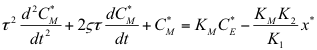SUMMARY
The discussion focuses on solving a second-order ordinary differential equation (ODE) in control systems, specifically with parameters Km = 0.5, K2 = 0.03, K1 = 0.05, and x* = 49. The auxiliary equation and general solution can be derived by assuming C_m = e^(kt) and substituting the given parameters. The values of τ (time constant) and ζ (damping ratio) are also critical in determining the system's behavior, and it is recommended to substitute parameter values for clarity in the equation.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of second-order ordinary differential equations (ODEs)
- Familiarity with control systems terminology
- Knowledge of exponential functions and their applications in differential equations
- Basic concepts of damping ratio (ζ) and time constant (τ)
NEXT STEPS
- Study the derivation of the auxiliary equation for second-order ODEs
- Learn about the significance of time constant (τ) and damping ratio (ζ) in control systems
- Explore analytical methods for solving ordinary differential equations
- Investigate the application of parameter substitution in simplifying differential equations
USEFUL FOR
Control systems engineers, students studying differential equations, and professionals involved in system dynamics and stability analysis.