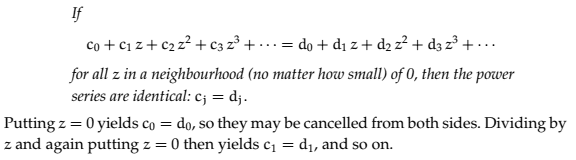Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around the validity of a proof related to the Identity Theorem for power series. Participants analyze the assumptions made when dividing by a variable and the implications for continuity and limits, particularly in the context of the neighborhood of zero.
Discussion Character
- Debate/contested
- Technical explanation
- Mathematical reasoning
Main Points Raised
- Some participants question the validity of the proof, noting that dividing by ##z## assumes ##z \neq 0##, which complicates the application of limits at ##z=0##.
- Others argue that the functions involved are analytic and continuous, allowing for the use of limits to establish equality at ##z=0##.
- One participant suggests that the theorem holds even if the series are equal only at an infinite sequence of points converging to ##0##.
- Another participant points out that the term "neighborhood" often leads to confusion regarding limits and the actual substitution of ##z=0##.
- Some participants emphasize the need for continuity at ##0## for the arguments to hold, suggesting that this continuity should be established prior to applying the theorem.
- A later reply introduces a simpler proposition that reinforces the idea that if a power series equals zero in a neighborhood of zero, all coefficients must be zero.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express differing views on the validity of the proof and the assumptions made. There is no consensus on whether the original proof is valid, as some find it sloppy while others defend its reasoning.
Contextual Notes
Participants note that the continuity of functions defined by power series at ##0## needs to be proven, which is typically established through uniform convergence on compact subsets within the circle of convergence.