Inertial force acceleration (vertical axis)
- Thread starter Justin71
- Start date
Click For Summary
SUMMARY
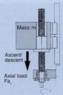
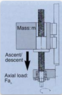
The discussion centers on the calculation of inertial force (Fi) in vertical and horizontal orientations. Participants clarify that the fundamental equation Fi = m.a applies regardless of the system's orientation. The total force (Fa) during vertical motion is expressed as Fa = Fm + Fg + Fi + Ff, with Ff being zero during ascent and descent. The gravitational force (Fg) is defined as Fg = mg.sin(Θ), emphasizing the need to account for gravitational effects when calculating forces in vertical motion.
PREREQUISITES- Understanding of Newton's Second Law (F=ma)
- Familiarity with force components: Inertial Force (Fi), Gravitational Force (Fg), and Frictional Force (Ff)
- Knowledge of torque calculations in mechanical systems
- Basic concepts of vector forces and their directions
- Study the effects of gravitational force on vertical motion in mechanical systems
- Learn about torque calculations using the formula T=(Fa x screw_lead)/(2*pi*efficiency)
- Explore the role of friction in force calculations during machine operations
- Investigate the implications of force directionality in engineering applications
Mechanical engineers, physics students, and anyone involved in the design and analysis of systems requiring force calculations in both vertical and horizontal orientations.
Similar threads
- · Replies 8 ·
- · Replies 15 ·
- · Replies 8 ·
- · Replies 1 ·
- · Replies 5 ·
- · Replies 2 ·
- · Replies 3 ·