Hello Debmnzl,
We are given the function:
$\displaystyle f(x)=a\ln(x)+\frac{1}{2}$
and are asked to compute its inverse. So, we may begin by switching $x$ and $f(x)$, and then solving for $f(x)$ which will actually be $\displaystyle f^{-1}(x)$
$\displaystyle x=a\ln(f(x))+\frac{1}{2}$
Subtract through by $\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}$
$\displaystyle x-\frac{1}{2}=a\ln(f(x))$
Get common denominator on the left:
$\displaystyle \frac{2x-1}{2}=a\ln(f(x))$
Divide through by $a$:
$\displaystyle \frac{2x-1}{2a}=\ln(f(x))$
Convert from logarithmic to exponential form:
$\displaystyle e^{\frac{2x-1}{2a}}=f(x)$
and so we have:
$\displaystyle f^{-1}(x)=e^{\frac{2x-1}{2a}}$
Now, as a means of checking our work, we may use the fact that we require:
$\displaystyle f\left(f^{-1}(x) \right)=f^{-1}(f(x))=x$
i) $\displaystyle f\left(f^{-1}(x) \right)=a\ln\left(e^{\frac{2x-1}{2a}} \right)+\frac{1}{2}=a\left(\frac{2x-1}{2a} \right)+\frac{1}{2}=x$
ii) $\displaystyle f^{-1}(f(x))=e^{\frac{2\left(a\ln(x)+\frac{1}{2} \right)-1}{2a}}=e^{\frac{2a\ln(x)}{2a}}=e^{\ln(x)}=x$
So, we know the inverse function we found is correct.
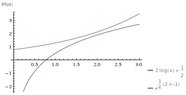
Next, we are instructed to let $a=2$ and sketch the graph. I will assume we are to graph both the given function and its inverse:
View attachment 613
Now, to find a value of $a$ such that the function and its inverse touch only once, we may use the fact that the two are reflected about the line $y=x$, and so must be tangent to this line.
The gradient of the line $y=x$ is 1, and so, we require:
$\displaystyle \frac{d}{dx}\left(f(x) \right)=\frac{a}{x}=1\,\therefore\,a=x$
$\displaystyle \frac{d}{dx}\left(f^{-1}(x) \right)=\frac{e^{\frac{2x-1}{2a}}}{a}=1\,\therefore\,a=e^{\frac{2x-1}{2a}}$
Now since we found $a=x$ we may write:
$\displaystyle a=e^{\frac{2a-1}{2a}}$
To compute the solution to this equation to 3 decimal places, we may use Newton's method. Let's define:
$\displaystyle g(a)=e^{\frac{2a-1}{2a}}-a=0$
where:
$\displaystyle g'(a)=\frac{1}{2a^2}e^{\frac{2a-1}{2a}}-1$
Newton's method gives us the recursion:
$\displaystyle a_{n+1}=a_n-\frac{g(a_n)}{g'(a_n)}$
Using the function we defined and its derivative, we have:
$\displaystyle a_{n+1}=a_n-\frac{e^{\frac{2a_n-1}{2a_n}}-a_n}{\frac{1}{2a_n^2}e^{\frac{2a_n-1}{2a_n}}-1}=\frac{a_n(1-2a_n)}{1-2a^2e^{\frac{1-2a_n}{2a_n}}}$
Using $a_0=2$ as our initial estimate, we then find:
$a_1\approx2.15910252177$
$a_2\approx2.15553677378$
$a_3\approx2.1555352035$
$a_4\approx2.1555352035$
Now, since we were only asked to find the estimate to 3 decimal places, we would write:
$a\approx2.156$
and since we found $a=x$ then the $y$-coordinate of the point of intersection must also be $a$ since the function and its inverse will touch along the line $y=x$
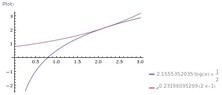
And so the point of intersection is approximately (2.156,2.156). Here is a graph using the better approximation we found:
View attachment 614