Joystar77
- 122
- 0
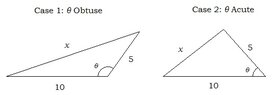
Math Problem: Find the length of the third side of a triangle if the area of the triangle is 18 and two of its sides have lengths of 5 and 10.
Which one of these are correct when I am working them out? If none of these are correct, then can somebody please help me solve this math problem step-by-step?
First way I worked out the problem:
A=18=0.5*5*10*sin(x)
x = 46 degrees
====
c^2 = 10^2+5^2-2*50*cos(46) = 55,53
third side:
c = 7,45
Second way I worked out the problem:
I know A = 18 units², a = 5 units, and b = 10 units
given A = (absin(C))/2
=> 18 = 25sin(C)
=> 18/25 = sin(C)
=> C = sin⁻¹(18/25)
given c² = a² + b² -2abcos(C)=> c² = 25 + 100 -100cos(sin⁻¹(18/25))
=> c = √(125 -100cos(sin⁻¹(18/25)))
=> c = √(125 - 4√301) units
=> c ≈ 7.4567 ( 4 dp)
Third way I worked out the problem:
Use Heron's formula for triangle:
Suppose the third side is x, and the others are 5 and 10, so by Heron formula, we get:
Area = sqrt(s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c))
where s=semi perimeter, a,b,c are sides of triangle, a=x, b=5, c=10
so, s=1/2.(x+5+10)
=1/2(x+15)
s-a= 1/2x +15/2 -x= 15/2-x/2
s-b=x/2+15/2-10/2=x/2+5/2
s-c=x/2+15/2-20/2=x/2-5/2
Area= sqrt(x/2+15/2)(15/2-x/2)(x/2+5/2)(x/2-5/…
324=(15/2+x/2)(15/2-x/2)(x/2+5/2)(x/2-…
324=(225/4 -x^2/4)(x^2/4-25/4)..multiply by 4 to get
1296=(225-x^2)(x^2-25)
225x^2-225*25-x^4+25x^2-1296=0
-x^4+250x^2-6921=0
-(x^4-250x^2+6921)=0
-((x^2-125)-8704)=0
(x^2-16sqrt34-125)(x^2+16sqrt34-125)=0
x^2=16sqrt34+125
x=sqrt(16sqrt 34+125)
=14.775
or
x^2=125-16sqrt34
x=sqrt(125-16sqrt34)
=5.63
So, the length of the third side is 14.775 or 5.63
I am really lost and confused on this problem.
Which one of these are correct when I am working them out? If none of these are correct, then can somebody please help me solve this math problem step-by-step?
First way I worked out the problem:
A=18=0.5*5*10*sin(x)
x = 46 degrees
====
c^2 = 10^2+5^2-2*50*cos(46) = 55,53
third side:
c = 7,45
Second way I worked out the problem:
I know A = 18 units², a = 5 units, and b = 10 units
given A = (absin(C))/2
=> 18 = 25sin(C)
=> 18/25 = sin(C)
=> C = sin⁻¹(18/25)
given c² = a² + b² -2abcos(C)=> c² = 25 + 100 -100cos(sin⁻¹(18/25))
=> c = √(125 -100cos(sin⁻¹(18/25)))
=> c = √(125 - 4√301) units
=> c ≈ 7.4567 ( 4 dp)
Third way I worked out the problem:
Use Heron's formula for triangle:
Suppose the third side is x, and the others are 5 and 10, so by Heron formula, we get:
Area = sqrt(s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c))
where s=semi perimeter, a,b,c are sides of triangle, a=x, b=5, c=10
so, s=1/2.(x+5+10)
=1/2(x+15)
s-a= 1/2x +15/2 -x= 15/2-x/2
s-b=x/2+15/2-10/2=x/2+5/2
s-c=x/2+15/2-20/2=x/2-5/2
Area= sqrt(x/2+15/2)(15/2-x/2)(x/2+5/2)(x/2-5/…
324=(15/2+x/2)(15/2-x/2)(x/2+5/2)(x/2-…
324=(225/4 -x^2/4)(x^2/4-25/4)..multiply by 4 to get
1296=(225-x^2)(x^2-25)
225x^2-225*25-x^4+25x^2-1296=0
-x^4+250x^2-6921=0
-(x^4-250x^2+6921)=0
-((x^2-125)-8704)=0
(x^2-16sqrt34-125)(x^2+16sqrt34-125)=0
x^2=16sqrt34+125
x=sqrt(16sqrt 34+125)
=14.775
or
x^2=125-16sqrt34
x=sqrt(125-16sqrt34)
=5.63
So, the length of the third side is 14.775 or 5.63
I am really lost and confused on this problem.