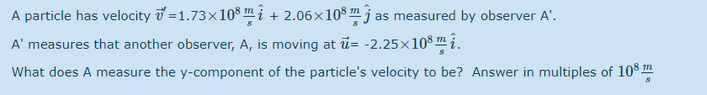JoeyBob
- 256
- 29
- Homework Statement
- see attached
- Relevant Equations
- u'=u/(δ(1-(uv)/c^2)
So for the formula, u'=u/(δ(1-(uv)/c^2)
u=2.06E8 and v=0. I am only looking at the y components here.
Since v=0 it really becomes u'=u/δ or u'= u*sqrt(1-(u^2)/c^2)).
Anyways when I plug this in I am getting 1.49E8 when the answer should be 0.951E8. Am I not using the correct formula here?
u=2.06E8 and v=0. I am only looking at the y components here.
Since v=0 it really becomes u'=u/δ or u'= u*sqrt(1-(u^2)/c^2)).
Anyways when I plug this in I am getting 1.49E8 when the answer should be 0.951E8. Am I not using the correct formula here?