SUMMARY
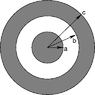
The discussion focuses on calculating the magnetic field of a coaxial cable with inner and outer conductors carrying equal and opposite currents of 5.00 A. The dimensions of the conductors are specified as a = 1.20 cm, b = 5.40 cm, and c = 7.30 cm. The magnetic field at a distance of 0.36 cm from the center axis is derived using Ampère's Law, specifically the equation \(\oint B \cdot dl = \mu_0 I_{\text{enclosed}}\). The correct approach involves recognizing that the magnetic field inside the inner conductor is proportional to the enclosed current, leading to the conclusion that the magnetic field strength must be recalculated considering the fraction of the current enclosed.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Ampère's Law and its application in magnetostatics
- Familiarity with coaxial cable geometry and current distribution
- Knowledge of magnetic field calculations in cylindrical coordinates
- Basic principles of electromagnetism, particularly magnetic fields generated by current-carrying conductors
NEXT STEPS
- Study the application of Ampère's Law in different geometries, particularly cylindrical systems
- Learn about the magnetic field calculations for coaxial cables in various configurations
- Explore the concept of current density and its implications in magnetic field calculations
- Investigate the effects of varying current magnitudes and directions on magnetic field strength
USEFUL FOR
Physics students, electrical engineers, and anyone studying electromagnetism or working with coaxial cables in practical applications.