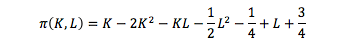Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around maximizing a profit function of two variables, K and L. Participants explore the necessary steps to find critical points and apply differentiation techniques to determine maximum profit, with a focus on understanding the mathematical process involved.
Discussion Character
- Homework-related
- Mathematical reasoning
Main Points Raised
- One participant requests explicit help with equations to solve for maximum profit.
- Another participant suggests finding critical points by setting the first partial derivatives to zero and using the second partials test for relative extrema.
- A participant expresses confusion and requests a simpler explanation, indicating a lack of understanding of the problem.
- There is a discussion about the profit function, with one participant questioning the presence of uncombined constant terms.
- One participant asserts confidence in the correctness of the profit function as stated.
- After clarification, the profit function is rewritten to combine constant terms, leading to a request for the first partial derivative with respect to K.
- Another participant mentions finding a similar example in their textbook, suggesting a potential understanding of the problem.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express varying levels of understanding, with some feeling lost while others show confidence in their grasp of the material. The discussion remains unresolved regarding the complete solution to the problem.
Contextual Notes
There are unresolved aspects regarding the differentiation process and the application of the second partials test, as well as the initial formulation of the profit function.