SUMMARY
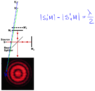
The discussion focuses on the behavior of fringes in a Michelson interferometer, specifically addressing the conditions under which a single light source can produce a pattern of fringes. It is established that diverging the laser beam using a lens allows for the observation of a "bullseye" pattern, despite the absence of diffraction. The phase difference between light rays from two mirrors creates varying brightness, leading to the formation of concentric rings. When the mirrors are equidistant, constructive interference results in a solid spot devoid of rings.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Michelson interferometer principles
- Knowledge of light interference and phase differences
- Familiarity with laser beam divergence techniques
- Basic geometry related to optics and wave behavior
NEXT STEPS
- Study the mathematical derivation of fringe patterns in Michelson interferometers
- Learn about laser beam divergence and its effects on interference patterns
- Explore the concept of constructive and destructive interference in optics
- Investigate the role of mirror alignment in interferometric experiments
USEFUL FOR
Physics students, optical engineers, and researchers interested in wave optics and interference phenomena will benefit from this discussion.