- 2,758
- 12,042
- TL;DR
- An anaerobic ciliate (a eukaryotic single cell organism) has been found with a non-mitochondrial derived endosymbiont that convert nitrate to nitrogen and produce ATP.
A ciliate containing a new endosymbiont has been found in a anaerobic (no oxygen) environment at the bottom of a lake, with high nitrate levels.
Nature news and views article here.
Nature research article here.
The ciliate is a eukaryote and would normally have inherited a mitochondrial endosymbiont. However, it lives in an anaerobic (oxygen free) environment and its mitochondrial endosymbiont has evolved (devolved) into a hydrogenosome (something that has happened, independently, more than once in other anaerobic ciliates). Hydrosomes use the less efficient fermentation set of reactions to generate ATP.
In this case, the ciliate was able to form an additional endosymbiotic relationship with a free living gammaproteobacterium that instead of using oxygen as an electron acceptor in it electron transport chain (ETC, like in mitochondria), it uses its ETC to make nitrogen from nitrate and produce ATP (denitrification).
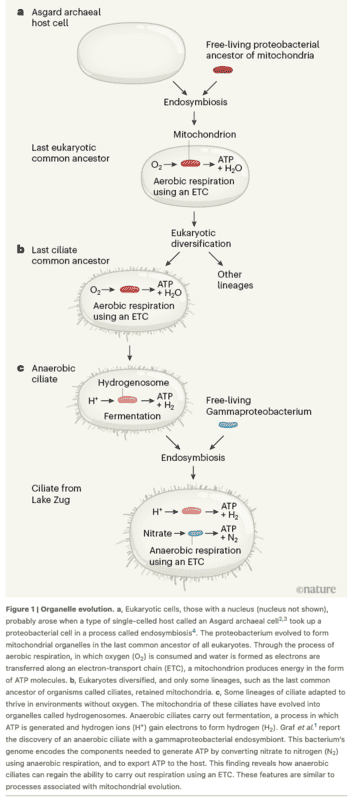
So, this ciliate has two kinds of endosymbionts, the hydrogenosome (degeneratively derived from a mitochondrion), as well as the ciliate's newly discovered denitrifying endosymbiont.
The denitrifying endosymbiont has a reduced genome of about 310 protein encoding genes, indicative of its status as an endosymbiont, but not as extreme a reduction as is found in the mitochondria (30-40 genes). E.coli bacteria for example, have about 4,000 genes. By living in the internal environment of another cell, the endosymbiont can take advantage of host cell's physiology and afford to lose redundant genes. However, it has not had as much evolutionary history in this environment as the mitochondria has had, so it has not been under these selective pressures as long.
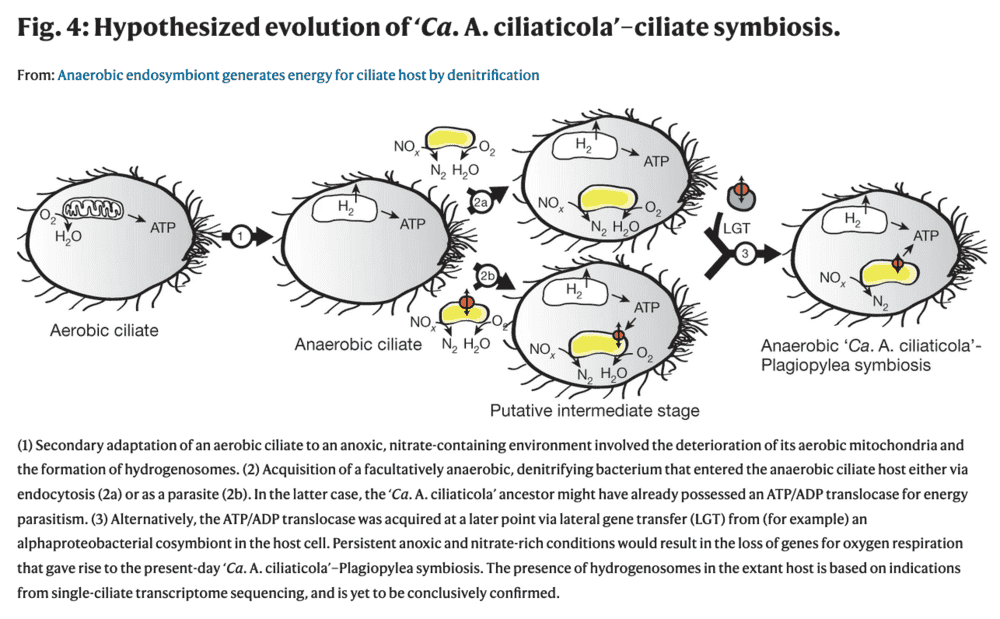
This second endosymbiotic event in this ciliate's evolutionary lineage, is similar to the eukaryotic cell precursors of plant cells, acquiring a second endosymbiont in the chloroplasts of today's plant cells.
Nature news and views article here.
Nature research article here.
The ciliate is a eukaryote and would normally have inherited a mitochondrial endosymbiont. However, it lives in an anaerobic (oxygen free) environment and its mitochondrial endosymbiont has evolved (devolved) into a hydrogenosome (something that has happened, independently, more than once in other anaerobic ciliates). Hydrosomes use the less efficient fermentation set of reactions to generate ATP.
In this case, the ciliate was able to form an additional endosymbiotic relationship with a free living gammaproteobacterium that instead of using oxygen as an electron acceptor in it electron transport chain (ETC, like in mitochondria), it uses its ETC to make nitrogen from nitrate and produce ATP (denitrification).
So, this ciliate has two kinds of endosymbionts, the hydrogenosome (degeneratively derived from a mitochondrion), as well as the ciliate's newly discovered denitrifying endosymbiont.
The denitrifying endosymbiont has a reduced genome of about 310 protein encoding genes, indicative of its status as an endosymbiont, but not as extreme a reduction as is found in the mitochondria (30-40 genes). E.coli bacteria for example, have about 4,000 genes. By living in the internal environment of another cell, the endosymbiont can take advantage of host cell's physiology and afford to lose redundant genes. However, it has not had as much evolutionary history in this environment as the mitochondria has had, so it has not been under these selective pressures as long.
This second endosymbiotic event in this ciliate's evolutionary lineage, is similar to the eukaryotic cell precursors of plant cells, acquiring a second endosymbiont in the chloroplasts of today's plant cells.
Last edited: