Cato11
- 46
- 11
- TL;DR
- Non-uniform Circular Motion & Acceleration
I would really appreciate some help with this problem regarding non-uniform circular motion, in which a body is accelerating as it follows a circular path.
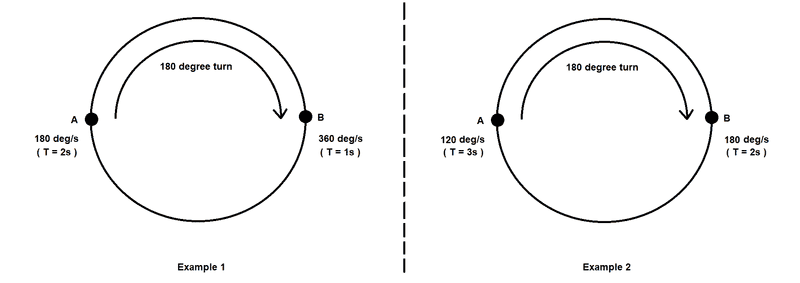
If we take Example 1, a body starts at Point A with an angular speed of 180°/s. The body accelerates to Point B and reaches it some time later with a new speed of 360°/s. Points A and B are exactly 180° apart. What I am trying to understand is:
1. If the body accelerated uniformly from Point A to Point B, how long did the travel time take between the two points?
2. How can we find out what the rate of uniform acceleration is between both points?
If we take Example 2, a body starts at Point A with an angular speed of 120°/s. The body accelerates to Point B and reaches it some time later with a new speed of 180°/s. Points A and B are still exactly 180° apart. The same questions above arise... how does it differ? My instinct tells me the travel time will be longer, with a slower rate of uniform acceleration.
If anyone could help me to answer the two questions I would be enormously grateful. Please comment if further clarification would help.
If we take Example 1, a body starts at Point A with an angular speed of 180°/s. The body accelerates to Point B and reaches it some time later with a new speed of 360°/s. Points A and B are exactly 180° apart. What I am trying to understand is:
1. If the body accelerated uniformly from Point A to Point B, how long did the travel time take between the two points?
2. How can we find out what the rate of uniform acceleration is between both points?
If we take Example 2, a body starts at Point A with an angular speed of 120°/s. The body accelerates to Point B and reaches it some time later with a new speed of 180°/s. Points A and B are still exactly 180° apart. The same questions above arise... how does it differ? My instinct tells me the travel time will be longer, with a slower rate of uniform acceleration.
If anyone could help me to answer the two questions I would be enormously grateful. Please comment if further clarification would help.