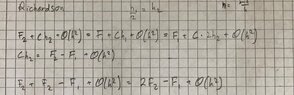SUMMARY
The discussion centers on the application of Richardson Extrapolation to Riemann Sums, specifically comparing its results to the Trapezoidal Rule for approximating the integral of sin(x) over the interval [0,1]. The user reports discrepancies in results, noting that while both methods share a convergence order of 2, they do not yield identical values. The key takeaway is that identical convergence orders do not guarantee equivalent results at intermediate steps, highlighting the importance of understanding the nuances of numerical methods.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of numerical integration techniques, specifically Riemann Sums and the Trapezoidal Rule.
- Familiarity with Richardson Extrapolation and its application in improving numerical estimates.
- Basic knowledge of calculus, particularly the properties of integrals and convergence.
- Proficiency in using mathematical software or programming languages for numerical analysis, such as R or Python.
NEXT STEPS
- Study the principles of Richardson Extrapolation in detail, focusing on its implementation in numerical methods.
- Explore the differences between various numerical integration techniques, including Simpson's Rule and their convergence properties.
- Learn how to implement Riemann Sums and the Trapezoidal Rule in R or Python for practical applications.
- Investigate error analysis in numerical integration to understand how convergence rates affect accuracy.
USEFUL FOR
Mathematicians, data scientists, and engineers involved in numerical analysis and computational methods who seek to enhance their understanding of integration techniques and their convergence behaviors.