SUMMARY
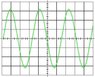
The discussion focuses on calculating the amplitude and frequency of a sinusoidal voltage displayed on an oscilloscope with a vertical sensitivity of 5mV/cm and a horizontal sensitivity of 0.5μs/cm. The amplitude is determined by multiplying the vertical sensitivity by the height of the waveform in centimeters, leading to a peak amplitude of approximately 16mV. For frequency, the period is calculated based on the horizontal divisions, with a period of 3.2 cm translating to a frequency of 312.5 Hz. The discussion clarifies common misconceptions regarding voltage units and emphasizes the importance of understanding oscilloscope readings.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of oscilloscope operation and sensitivity settings
- Familiarity with voltage measurement units (mV vs. MV)
- Knowledge of sinusoidal wave properties (amplitude, frequency, period)
- Basic skills in unit conversion and calculations
NEXT STEPS
- Learn how to interpret oscilloscope waveforms and measurements
- Study the relationship between period and frequency in sinusoidal signals
- Explore advanced oscilloscope features, such as triggering and persistence
- Investigate common pitfalls in voltage unit conversions and calculations
USEFUL FOR
Electronics students, engineers, and technicians who work with oscilloscopes and need to analyze voltage waveforms accurately.