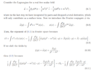Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around the path integral approach to deriving the Klein-Gordon propagator, focusing on specific steps and calculations presented in lecture notes. Participants are addressing issues related to the integration process and the resulting expressions, particularly concerning Dirac delta functions and the correct formulation of the propagator.
Discussion Character
- Technical explanation
- Mathematical reasoning
- Debate/contested
Main Points Raised
- One participant expresses confusion about deriving a Dirac delta function from their lecturer's notes, particularly in relation to a specific equation (6.9) and the integration process leading to a delta function.
- Another suggests replacing the current source and field with their Fourier transforms to achieve the desired delta function, emphasizing the need for separate momentum space variables.
- A third participant notes the necessity of using different dummy integration 4-momenta for each factor of the field in the integral, leading to a specific delta function result when integrating over spacetime.
- One participant acknowledges progress in deriving part of the expression but questions the manipulation of momentum variables in the second term of the equation.
- Another participant critiques a specific equation (6.10) as nonsensical, arguing that it fails to specify the propagator correctly and highlights the importance of the Feynman propagator's formulation, including the crucial ##\mathrm{i} 0^+## term.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express differing views on the correctness of certain expressions and the necessity of specific terms in the propagator's formulation. There is no consensus on the resolution of these issues, indicating ongoing debate.
Contextual Notes
Participants have not resolved the assumptions underlying the derivations, and there are indications of missing steps or definitions that could clarify the discussion further.