Click For Summary
SUMMARY
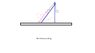
The discussion centers on calculating the tension T in a string within a physics problem involving forces. Key concepts include the use of the equation F = ma, and the importance of identifying forces such as gravity, tension, and friction. The coefficients of kinetic and static friction are specified as 0.15 and 0.30, respectively, which are critical for solving the problem accurately. Participants emphasize the necessity of a Free Body Diagram to visualize the forces acting on each body involved in the scenario.
PREREQUISITES- Understanding of Newton's Second Law (F = ma)
- Knowledge of Free Body Diagrams
- Familiarity with friction coefficients (kinetic and static)
- Basic trigonometry skills
- Study how to construct Free Body Diagrams for complex systems
- Learn about the implications of friction in tension calculations
- Explore advanced applications of Newton's laws in real-world scenarios
- Review examples of tension problems in physics textbooks
Students studying physics, particularly those focusing on mechanics and tension problems, as well as educators looking for examples of force analysis in classroom settings.
Similar threads
- · Replies 12 ·
- · Replies 18 ·
- · Replies 12 ·
- · Replies 1 ·
- · Replies 22 ·
- · Replies 4 ·