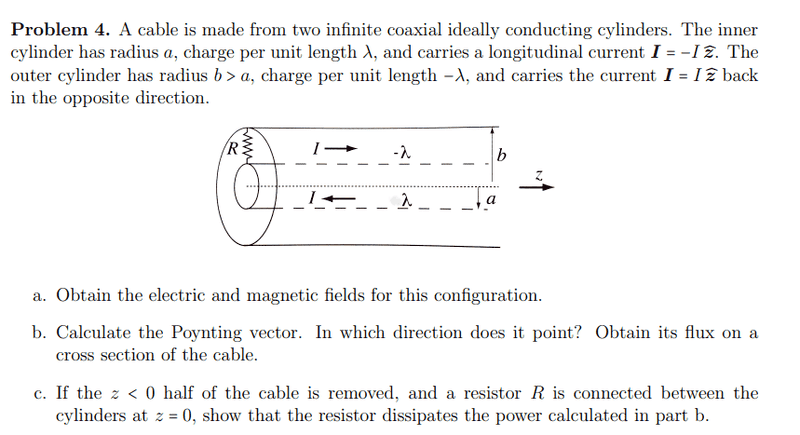
SUMMARY
The discussion focuses on calculating the power dissipated by a resistor connected between two cylinders in a coaxial cable setup. The key point is that for any resistance value R, the power dissipation must equal the rate of electromagnetic field energy propagation, determined using the Poynting vector from part (b). The relationship between voltage (V), current (I), and resistance (R) is established through Ohm's Law (V = IR), emphasizing the need for specific values of λ (wavelength) and I (current) to satisfy this equation. The problem is noted as poorly stated, leading to confusion among participants.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Poynting vector in electromagnetic theory
- Familiarity with Ohm's Law (V = IR)
- Knowledge of coaxial cable structure and properties
- Basic principles of dimensional analysis
NEXT STEPS
- Study the application of the Poynting vector in electromagnetic wave propagation
- Review the principles of resistance in electrical circuits
- Explore the characteristics of coaxial cables and their applications
- Investigate dimensional analysis techniques in physics problems
USEFUL FOR
Electrical engineers, physics students, and anyone involved in electromagnetic theory or coaxial cable design will benefit from this discussion.