Salmone
- 101
- 13
I have some questions on Franck Condon principle:
1. The principle states that if a molecule absorbs a photon of the appropriate energy, we could have both electronic and vibrational transitions and that is more likely to have a vibrational transition between states that have two "similar" wavefunctions. The first question is:
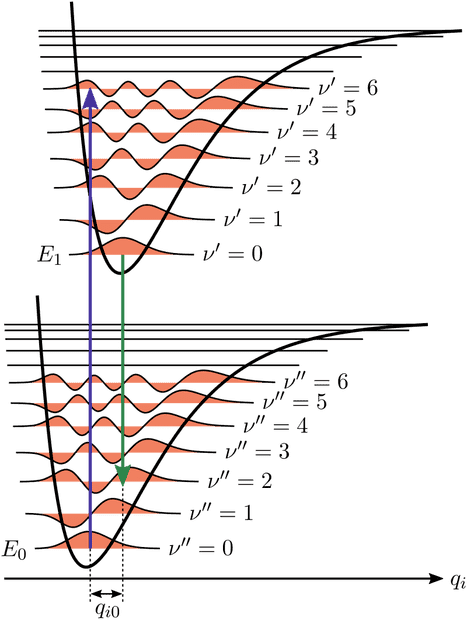
It is ok to me that it is more likely to have a vibrational transition between states that have two "similar" wavefunctions but of course if we see a transition between ##\nu=0## state and ##\nu'=5## state means that the absorbed photon had at least the energy separating ##\nu''=0## and ##\nu'=6##, right? With reference to the image, the "blue arrow transition" is more lilely to happen but we need a photon with the right energy, more or equal to the "lenght" of the arrow, right?
2. If the energy of the incoming photon is enough for that transition, is it mandatory for the molecule to also have a vibrational transition or it can jump just from electronic G.S. to electronic first excited state remaining on the same vibrational level?
3. Again with reference to the image, the potential drawn higher refers to an excited electronic state, if we are talking about molecules, what do we precisely mean by that? If just one electron of the electronic clouds is excited by a photon, the new arrangement of the molecule need to be drawn higher than the ground state in which all electrons were in their ground states? And, if two photons are excited, the new potential must be drawn as a different one much higher? Same if three electrons are excited or two electrons are excited to second excited state or third excited state?
1. The principle states that if a molecule absorbs a photon of the appropriate energy, we could have both electronic and vibrational transitions and that is more likely to have a vibrational transition between states that have two "similar" wavefunctions. The first question is:
It is ok to me that it is more likely to have a vibrational transition between states that have two "similar" wavefunctions but of course if we see a transition between ##\nu=0## state and ##\nu'=5## state means that the absorbed photon had at least the energy separating ##\nu''=0## and ##\nu'=6##, right? With reference to the image, the "blue arrow transition" is more lilely to happen but we need a photon with the right energy, more or equal to the "lenght" of the arrow, right?
2. If the energy of the incoming photon is enough for that transition, is it mandatory for the molecule to also have a vibrational transition or it can jump just from electronic G.S. to electronic first excited state remaining on the same vibrational level?
3. Again with reference to the image, the potential drawn higher refers to an excited electronic state, if we are talking about molecules, what do we precisely mean by that? If just one electron of the electronic clouds is excited by a photon, the new arrangement of the molecule need to be drawn higher than the ground state in which all electrons were in their ground states? And, if two photons are excited, the new potential must be drawn as a different one much higher? Same if three electrons are excited or two electrons are excited to second excited state or third excited state?
Last edited by a moderator: