SUMMARY
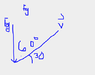
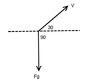
The gravitational force is doing work on a 2.0 kg projectile at a rate of -39 W when the projectile's velocity is 4.0 m/s at an angle of 30 degrees above the horizontal. The calculation involves using the equation for power, P = W/T, where work is derived from the gravitational force and the angle between the force and velocity vectors. The angle used in the calculations is 120 degrees, which is determined by the relationship between the gravitational force and the projectile's velocity direction. Understanding the vector components and the definition of work is crucial for accurate calculations.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of gravitational force and its calculation (9.8 m/s²).
- Familiarity with the concept of power in physics (P = W/T).
- Knowledge of vector components and angles in physics.
- Ability to interpret and draw force diagrams accurately.
NEXT STEPS
- Study the relationship between force, work, and power in physics.
- Learn how to accurately draw and interpret force diagrams.
- Explore the concept of work done by varying forces at different angles.
- Practice problems involving gravitational force and projectile motion.
USEFUL FOR
Students studying physics, particularly those focusing on mechanics and the concepts of work and energy, as well as educators looking for effective ways to teach these principles.