SUMMARY
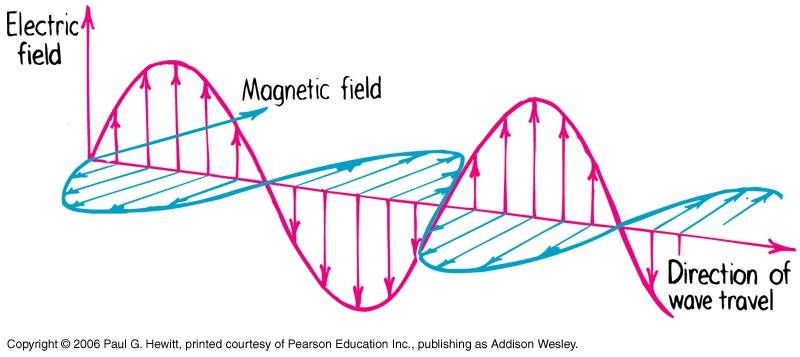
The relationship between the electric field and the probability amplitude of photons is complex and fundamentally different from classical wave descriptions. While electromagnetic waves are governed by Maxwell's equations, photons are described by quantum mechanics, specifically through Fock states and field operators. The intensity of both the electric field and probability amplitude is proportional to their respective squares, but they are not directly proportional due to their differing natures as a vector and a scalar. The electric field is represented by the operator ##\tilde{E}##, and its average value is calculated using the photon state ##|\psi\rangle##.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Maxwell's equations for electromagnetic waves
- Familiarity with quantum mechanics concepts, particularly Fock states
- Knowledge of field operators in quantum field theory
- Basic comprehension of the Schrödinger equation and its applications
NEXT STEPS
- Study the relationship between electric fields and quantum states in quantum field theory
- Learn about Fock states and their applications in quantum mechanics
- Explore the implications of the Schrödinger equation for relativistic particles
- Investigate the Riemann–Silberstein vector and its relevance to electromagnetic theory
USEFUL FOR
Physicists, quantum mechanics students, and researchers interested in the intersection of classical electromagnetism and quantum theory.