- #1
Vincent Mazzo
- 5
- 0
Hello guys
How can I calculate the following stiffness of the springs/suspensions in the case of inclined suspension (angle between suspension and axle)?
I know that the lateral separation of the springs causes them to develop a roll resisting moment proporcional to the difference roll angle between the body and the axle.
And in the case of independent suspension? How substitute the rate at the wheel for K_s and use the tread as the separation distance?
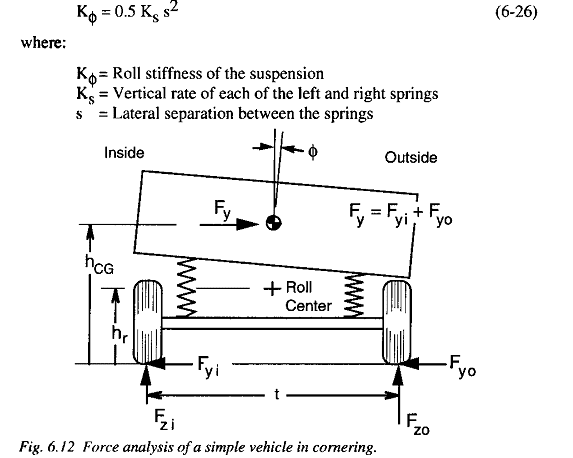
How can I calculate the following stiffness of the springs/suspensions in the case of inclined suspension (angle between suspension and axle)?
I know that the lateral separation of the springs causes them to develop a roll resisting moment proporcional to the difference roll angle between the body and the axle.
And in the case of independent suspension? How substitute the rate at the wheel for K_s and use the tread as the separation distance?
