- #1
nucloxylon
- 11
- 0
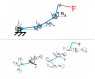
if i have a three link massless manipulator (each with length l1 l2 l3) that has rotational springs at each joint, k1 k2 k3, and I apply a force on the third link, what will be the joint angles at equilibrium?
do I find the lever arm to each joint and multiply that by the force to find the angles?
do I find the lever arm to each joint and multiply that by the force to find the angles?
Last edited: