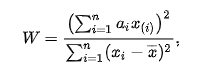Discussion Overview
The discussion centers around the interpretation of the order statistic in the context of the Shapiro-Wilk test, specifically regarding the relationship between the order statistic notation and the sorted data values.
Discussion Character
Main Points Raised
- One participant questions whether the notation $x_{(i)}$ (the ith order statistic) is equivalent to $x_i$ when the data is sorted in ascending order.
- Another participant confirms that if the data is sorted, then $x_{(i)} = x_i$ holds true.
- Some participants reference the Wikipedia page on the Shapiro-Wilk test, noting that it states $x_{(i)} \neq x_i$ in general.
- There is a recognition that for ordered sequences, the equality $x_{(i)} = x_i$ simplifies computations, which one participant found beneficial while debugging their implementation in Python.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express some agreement on the special case where $x_{(i)} = x_i$ for sorted data, but there is also acknowledgment of the general case where this does not hold, indicating a lack of consensus on the broader implications.
Contextual Notes
Participants reference the Wikipedia page for clarification, which introduces potential limitations in understanding the notation and its implications in different contexts.