member 731016
- Homework Statement
- Please see below
- Relevant Equations
- Please see below
For this problem,
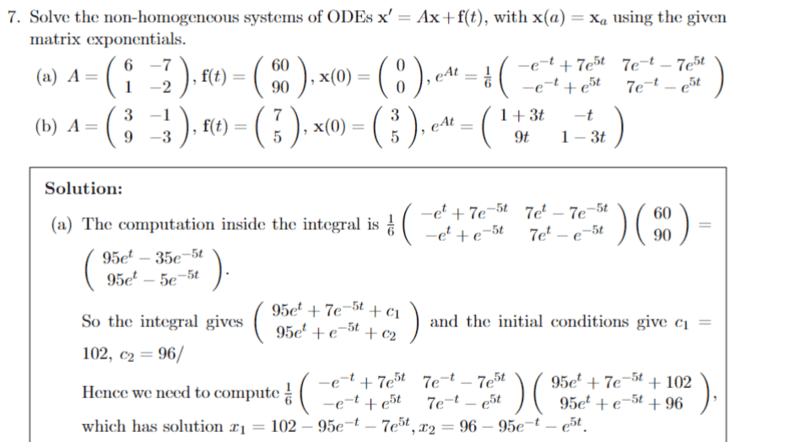
I don't understand why they include the constants of integration ##c_1 and c_2##, since the formula that we are meant to be using is ##\vec x = e^{At}c + e^{At}\int_{t_0}^{t} e^{-As} F(s)~ds## so we already have the integration variables. Does anybody please know why?
Thanks!
I don't understand why they include the constants of integration ##c_1 and c_2##, since the formula that we are meant to be using is ##\vec x = e^{At}c + e^{At}\int_{t_0}^{t} e^{-As} F(s)~ds## so we already have the integration variables. Does anybody please know why?
Thanks!