SUMMARY
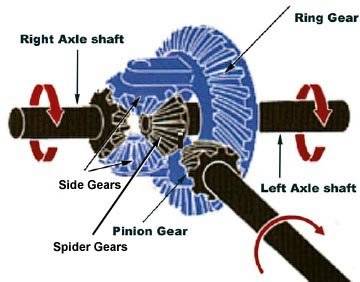
The discussion centers on the mechanics of spider gear rotation within a differential during vehicle cornering. When a car turns, the inner wheel travels a shorter distance than the outer wheel, leading to differing speeds. This difference creates opposing torques on the inner and outer wheels, which in turn causes the spider gears to rotate. The inner wheel experiences a "backwards" torque while the outer wheel receives a "forwards" torque, facilitating the necessary adjustments in wheel speed until a steady state is achieved.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of automotive differentials
- Knowledge of torque and its effects on rotational motion
- Familiarity with friction forces in mechanical systems
- Basic principles of vehicle dynamics during cornering
NEXT STEPS
- Research the mechanics of automotive differentials and their components
- Study the effects of torque on wheel performance in cornering scenarios
- Explore animations and visual aids on HOWSTUFFWORKS regarding differential operation
- Learn about resistive and input torques in mechanical systems
USEFUL FOR
Automotive engineers, mechanics, and enthusiasts interested in understanding the dynamics of vehicle handling and differential mechanics during cornering.