jstone326
- 1
- 0
Homework Statement
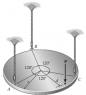
The circular plate has a weight W and a center of gravity at its center. If it is supported vy three vertical cords tied to its edge, determine the largest distance d from the center to where any vertical force P can be applied so as not to cause the force in anyone of the cables to become zero.
(see image)
Homework Equations
sum of Moments about somewhere are equal to 0
The Attempt at a Solution
I'm pretty lost as to how to start this problem. I think that I have to assume one of the tensions = 0, and that P would be located half way between C and A, thus making the angle between d and A/center = 60
Any help on how to approach this would be much appreciated.
Thanks