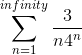SUMMARY
The discussion focuses on calculating the sum of an infinite series, specifically the series represented by 3*sigma(1/n*4^n). Participants clarify that this is not a geometric series due to the non-constant ratio between successive terms. Instead, they suggest using the Taylor series approach to transform the series into a recognizable form. Key techniques include differentiating or integrating known series, particularly the series for F(x) = ∑(x^n/n), which is essential for solving such problems.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of infinite series and convergence
- Familiarity with Taylor series and their applications
- Basic calculus concepts, including differentiation and integration
- Knowledge of logarithmic series and their properties
NEXT STEPS
- Study the properties of Taylor series and their convergence criteria
- Learn how to differentiate and integrate power series
- Explore the relationship between logarithmic functions and infinite series
- Review examples of transforming series into known forms for easier evaluation
USEFUL FOR
Students in calculus, mathematicians dealing with series convergence, and educators looking for effective methods to teach infinite series summation techniques.