Discussion Overview
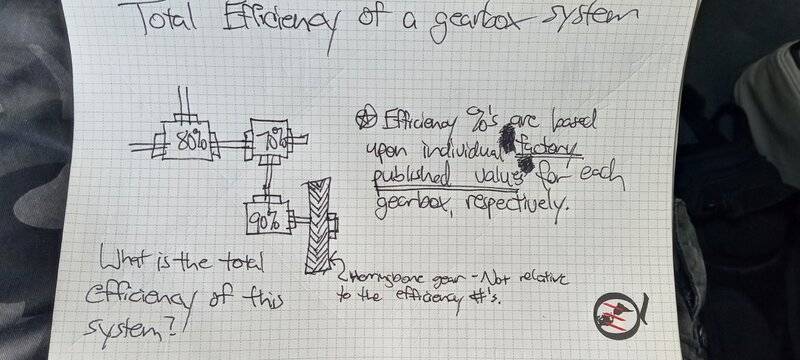
The discussion centers on determining the overall efficiency of a system of gearboxes, exploring how to calculate this efficiency given individual gearbox efficiencies. Participants consider different methods of calculation and the impact of gearbox types on efficiency.
Discussion Character
- Technical explanation
- Debate/contested
- Conceptual clarification
Main Points Raised
- One participant suggests that to find the overall efficiency of a series of gearboxes, one should multiply the efficiencies rather than averaging them.
- Another participant provides an example with 16 gearboxes, each at 90% efficiency, arguing that the actual efficiency is significantly lower due to cumulative losses.
- There is a question about whether the type of gearbox affects efficiency, with a participant noting that different types (planetary, worm, helical) have varying efficiencies.
- One participant mentions that a two-step reduction box is generally less efficient than a one-step reduction, despite the latter being heavier for the same power ratio.
- Discussion includes the impact of bearings on efficiency, particularly under side forces, and how planetary gears can mitigate these forces.
- Another participant raises the inefficiency of worm gears when driven backwards, suggesting that gearbox design influences overall performance.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express differing views on how to calculate overall efficiency, with some advocating for multiplication of efficiencies and others suggesting averaging. There is also no consensus on the impact of gearbox type on efficiency, as various factors are discussed without agreement.
Contextual Notes
Participants mention assumptions about gearbox types and their efficiencies, but do not provide a unified definition or framework for these calculations. The discussion includes unresolved mathematical steps and varying interpretations of efficiency metrics.
Who May Find This Useful
Individuals interested in mechanical engineering, particularly those focused on gearbox design and efficiency calculations, may find this discussion relevant.