SUMMARY
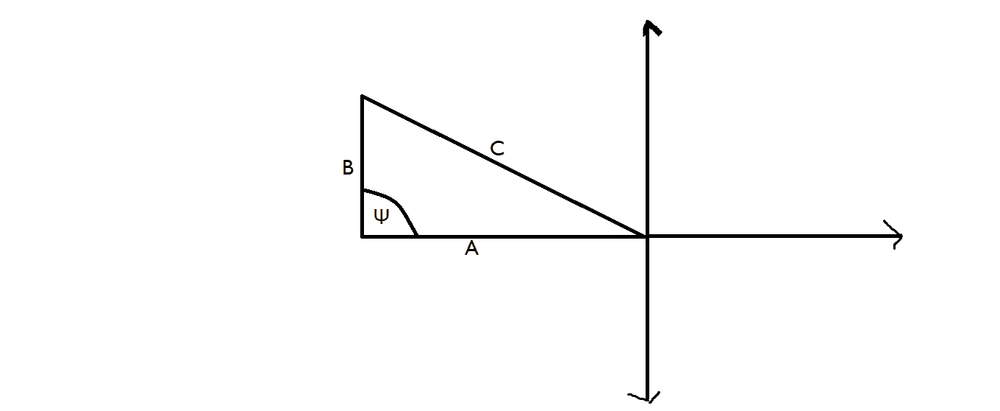
The discussion centers on the connection between the Law of Cosines and Euclid's teachings, particularly in the context of right-angled triangles. It establishes that for a right triangle, the Law of Cosines simplifies to \(C^2 = A^2 + B^2\) because \(\cos(90^{\circ}) = 0\). Participants highlight the importance of understanding trigonometric functions through the unit circle and the historical context of Euclid's Elements, specifically propositions 12 and 13 from Book II. The conversation emphasizes the geometric interpretation of the cosine function and its derivation from the Pythagorean theorem.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of trigonometric functions, specifically sine and cosine.
- Familiarity with the unit circle and its significance in trigonometry.
- Knowledge of the Pythagorean theorem and its application in geometry.
- Basic understanding of Euclidean geometry, particularly Euclid's Elements.
NEXT STEPS
- Study the derivation of the Law of Cosines in various trigonometry textbooks.
- Explore the unit circle and its applications in determining trigonometric values.
- Review propositions 12 and 13 from Book II of Euclid's Elements for a deeper understanding of geometric proofs.
- Investigate the historical context of trigonometric functions and their development in mathematics.
USEFUL FOR
Mathematicians, educators, students of geometry and trigonometry, and anyone interested in the historical foundations of mathematical concepts.