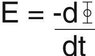SUMMARY
Faraday's Law describes the relationship between magnetic flux and induced electromotive force (emf) in a closed loop. The term E represents the induced electromotive force, while the notation -d/dt signifies the negative time derivative of the magnetic flux (φ) through the loop. Understanding these components is crucial for grasping the principles of electromagnetic induction. The equation illustrates that a change in magnetic flux over time results in an induced emf, which is fundamental in electrical engineering and physics.
PREREQUISITES
- Basic understanding of electromagnetic induction
- Familiarity with calculus, specifically derivatives
- Knowledge of magnetic flux concepts
- Understanding of electrical circuits and current (I)
NEXT STEPS
- Study the mathematical derivation of Faraday's Law
- Learn about Lenz's Law and its application in electromagnetic systems
- Explore practical applications of Faraday's Law in generators and transformers
- Investigate the relationship between magnetic fields and electric currents
USEFUL FOR
Students of physics, electrical engineers, and anyone interested in the principles of electromagnetic induction and their applications in technology.