Discussion Overview
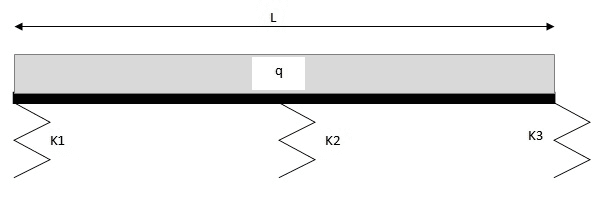
The discussion revolves around the problem of analyzing a beam supported by three different springs under a uniform distributed load. Participants explore various methods and considerations for solving this statically indeterminate problem, including the effects of spring elasticity and rigid body movement.
Discussion Character
- Technical explanation
- Debate/contested
- Mathematical reasoning
Main Points Raised
- Some participants note that the problem is statically indeterminate and requires more than the two equations of static equilibrium to find reactions in each spring.
- There is a discussion about the need to consider the deflection of the beam at the supports due to the elasticity of the springs, which complicates the calculations.
- Some suggest that methods for analyzing beams on elastic supports exist, but they may not be sufficient for cases with multiple springs.
- One participant mentions that the presence of multiple springs introduces rigid body movement, making the solution less intuitive and more complex.
- Another proposes using superposition to solve the problem if the spring constants are known, referencing an article with a relevant example.
- There is a suggestion to analyze the beam as rigid if the stiffness of the springs is significantly different from that of the beam.
- Some participants express uncertainty about the applicability of superposition, noting that it may not assume the beam is a rigid body.
- One participant argues that the problem may relate to "Beams on elastic foundation" and should be approached differently.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express differing views on the best approach to solve the problem, with no consensus reached on a single method. There are competing ideas regarding the use of superposition and the treatment of the beam's rigidity.
Contextual Notes
Participants highlight the complexity introduced by multiple springs and the need for specific spring constants, indicating that assumptions about stiffness and interactions may affect the analysis.