maxim07
- 53
- 8
- Homework Statement
- What value of z makes the curve have more than one stationary point
- Relevant Equations
- f(x) = 2x^3 -12x^2 + zx + 30
Here is my attempt at a solution
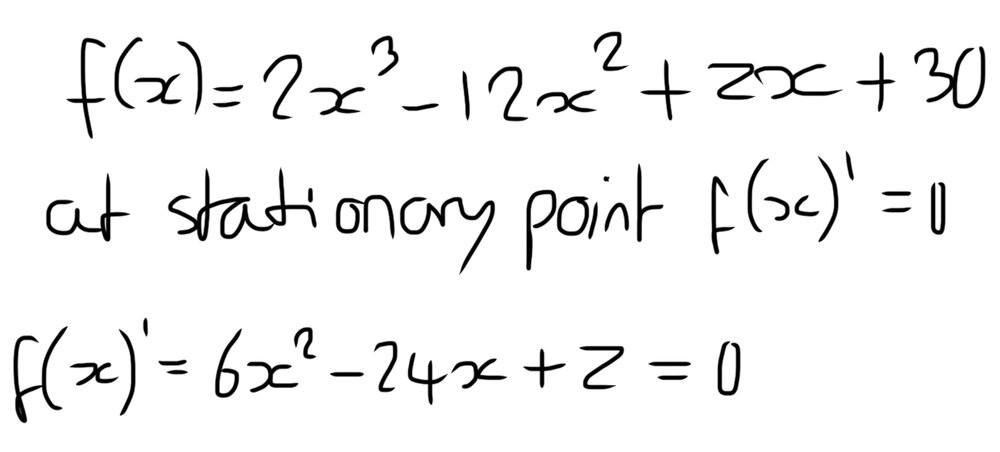
I don’t know where to go from here, as the equation is a quadratic it will have two solutions which means there will be two stationary points, but I don’t know how to solve for z.
I don’t know where to go from here, as the equation is a quadratic it will have two solutions which means there will be two stationary points, but I don’t know how to solve for z.