SUMMARY
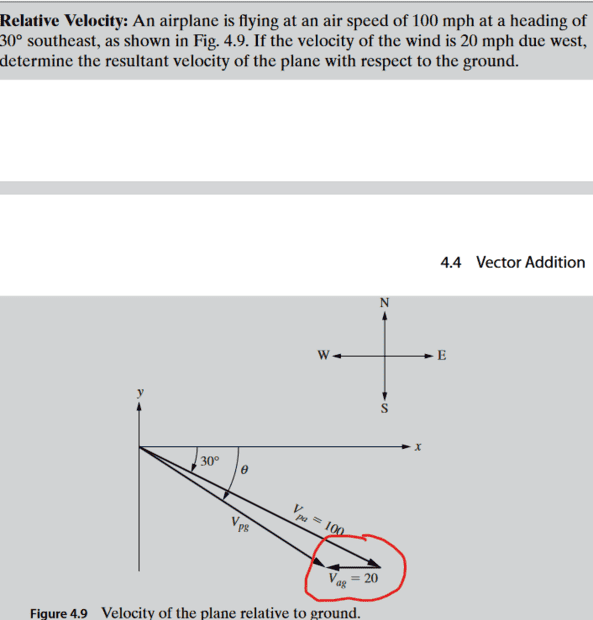
The discussion centers on vector addition and the determination of angles in relation to the positive x-axis. It establishes that the angle Vag is 180° when the vector points left, and clarifies that simply adding angles, such as 30° and 150°, does not yield the resultant angle relative to the x-axis. The conversation emphasizes the importance of resolving vectors into components, calculating magnitudes, and applying the vector addition rule, specifically stating that for vectors A and B, the resultant vector C is defined by C_x = A_x + B_x and C_y = A_y + B_y.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of vector components and their resolution
- Familiarity with trigonometric functions: sine and cosine
- Knowledge of the Pythagorean theorem for calculating vector magnitudes
- Basic grasp of tangent function for determining angles
NEXT STEPS
- Study vector resolution techniques in physics
- Learn how to apply the Pythagorean theorem in vector calculations
- Explore the use of trigonometric identities in vector analysis
- Investigate practical applications of vector addition in physics problems
USEFUL FOR
Students and professionals in physics, engineering, and mathematics who are looking to deepen their understanding of vector addition and angle determination in two-dimensional space.