cbarker1
Gold Member
MHB
- 345
- 23
Dear Everyone,
A sphere is attached to the ceiling of an elevator by a string. A second sphere is attached to the first one by a second string. Both strings are of negligible mass. Here $m_1=m_2=m=3.52\text{ kg}$.
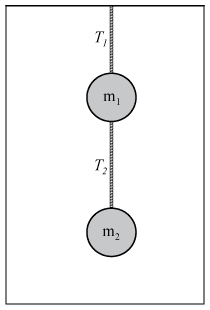
(a) The elevator starts from rest and accelerates downward with $a=1.45\,\dfrac{\text{m}}{\text{s}^2}$. What are the tensions in the two strings?
(b) If the elevator starts from rest and accelerates upward with the same acceleration, what will be the tension in the two strings?
(c) The maximum tension the two strings can withstand is 80.0 N. What maximum upward acceleration can the elevator have without having one of the strings break?
I would need to some help to setup and find the value of Tension of the cable one.
Thanks,
Cbarker1
A sphere is attached to the ceiling of an elevator by a string. A second sphere is attached to the first one by a second string. Both strings are of negligible mass. Here $m_1=m_2=m=3.52\text{ kg}$.

(a) The elevator starts from rest and accelerates downward with $a=1.45\,\dfrac{\text{m}}{\text{s}^2}$. What are the tensions in the two strings?
(b) If the elevator starts from rest and accelerates upward with the same acceleration, what will be the tension in the two strings?
(c) The maximum tension the two strings can withstand is 80.0 N. What maximum upward acceleration can the elevator have without having one of the strings break?
I would need to some help to setup and find the value of Tension of the cable one.
Thanks,
Cbarker1