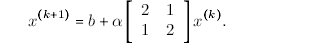Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around determining the values of α for any initial value of x(0) in a linear system, particularly focusing on convergence criteria and numerical stability. Participants explore mathematical formulations and implications related to iterative methods.
Discussion Character
- Technical explanation, Mathematical reasoning, Debate/contested
Main Points Raised
- Some participants suggest that the question pertains to numerical stability, proposing that the absolute value of α times the norm of the matrix must be less than 1 for stability.
- Others emphasize the need to find values of α that ensure convergence of the iteration process.
- A participant references a first-order difference equation and provides a general solution involving α, suggesting a specific context involving vectors and matrices.
- Another participant reiterates the convergence condition, stating that ||αA|| must be less than 1, leading to the conclusion that |α| must be less than 1/||A||.
- Participants engage in mathematical derivations to illustrate how the distance from the limit affects convergence.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
There is no consensus on the specific values of α, but participants generally agree on the conditions necessary for convergence and stability, with multiple approaches and interpretations presented.
Contextual Notes
The discussion includes various assumptions about the nature of the matrix A and the initial conditions, which may affect the convergence criteria. Some mathematical steps and definitions remain unresolved.
Who May Find This Useful
Readers interested in numerical methods, linear systems, and convergence criteria in iterative processes may find this discussion relevant.