Benjamin_harsh
- 211
- 5
- Homework Statement
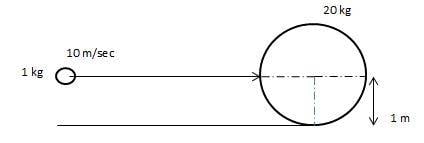
- A 1 kg mass of clay, moving with a velocity of 10 m/s, strickes a stationary wheel and sticks to it. The solid wheel has a mass of 20 kg and a radius of 1m. Assuming that the wheel is set into pure rolling motion, the angular velocity of the wheel immediately after the impact is approximately.
- Relevant Equations
- ##L_{i} = mvr = 1*10*1 = 10##,
##L_{f} = mv_{cm}r + Iω##
A 1 kg mass of clay, moving with a velocity of 10 m/s, strickes a stationary wheel and sticks to it. The solid wheel has a mass of 20 kg and a radius of 1m. Assuming that the wheel is set into pure rolling motion, the angular velocity of the wheel immediately after the impact is approximately.

Sol:
##L_{i} = mvr = 1*10*1 = 10##
##L_{f} = mv_{cm}r + Iω##
##= 20*rω*r + (mr^2 ω)/2 = 20ω + 10ω##
##L_{f} =30 ω##
##L_{i} = Lf##
##10 = 30 ω##
##ω = \large\frac {1}{3} \;\normalsize rad/sec##
What are these two: ##L_{i}## & ##L_{f}##?
Sol:
##L_{i} = mvr = 1*10*1 = 10##
##L_{f} = mv_{cm}r + Iω##
##= 20*rω*r + (mr^2 ω)/2 = 20ω + 10ω##
##L_{f} =30 ω##
##L_{i} = Lf##
##10 = 30 ω##
##ω = \large\frac {1}{3} \;\normalsize rad/sec##
What are these two: ##L_{i}## & ##L_{f}##?