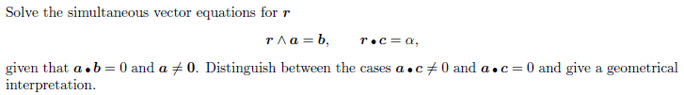GreenGoblin
- 68
- 0
I am assigned the following problem,
"Solve the simultaneous vector eqs. for r:
r \times a = b, r \centerdot c = \alpha
given that a \centerdot b = 0 and a \neq 0
Distinguish between a \centerdot c equal 0 and not equal 0, and give geometrical interpretation on this."
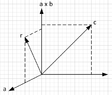
OK then. First problem.. is it not obvious a \centerdot b = 0? Since b is the cross-product of r and a. We know already that a and b are perpendicular.
SO. Main problem.. I don't know what I am actually looking to solve here. Should I be aiming to isolate r as a function of these assorted other things? IS that the form of the solution required?
AS WELL. What does distinguish mean in a mathematical context? How can I, in a formal manner, 'distinguish' something?
Gracias,
Green Goblin
TESTTESTTESTTESTTESTTESTTESTTESTTESTTEST
"Solve the simultaneous vector eqs. for r:
r \times a = b, r \centerdot c = \alpha
given that a \centerdot b = 0 and a \neq 0
Distinguish between a \centerdot c equal 0 and not equal 0, and give geometrical interpretation on this."
OK then. First problem.. is it not obvious a \centerdot b = 0? Since b is the cross-product of r and a. We know already that a and b are perpendicular.
SO. Main problem.. I don't know what I am actually looking to solve here. Should I be aiming to isolate r as a function of these assorted other things? IS that the form of the solution required?
AS WELL. What does distinguish mean in a mathematical context? How can I, in a formal manner, 'distinguish' something?
Gracias,
Green Goblin
TESTTESTTESTTESTTESTTESTTESTTESTTESTTEST
Last edited: