- #1
Olivia Lam
- 2
- 1
- Homework Statement
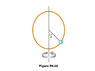
- A circular hoop rotates with uniform angular velocity w about a vertical diameter AOB, O being the center. A smooth ring P of mass m can slide on the hoop. If θ be the angle of inclination of the radius OP to the vertical when the ring is in equilibrium with respect to the hoop, (a) find cos θ in terms of the radius of the hoop r, angular velocity w and g. (b) Find the reaction force between the ring and the hoop.
- Relevant Equations
- N cos θ=mg
N sin θ=mrw^2 sin θ
cos θ=g/rw^2
a.)N cos θ=mg
N sin θ=mrw^2 sin θ
cos θ=g/rw^2
b.) My question is reaction force =N ? or =F=mg tanθ ?
If it is N then N=mg cosθ =mg^2/r w^2 or N=mg/cosθ =mrw^2 ?
Thank you
N sin θ=mrw^2 sin θ
cos θ=g/rw^2
b.) My question is reaction force =N ? or =F=mg tanθ ?
If it is N then N=mg cosθ =mg^2/r w^2 or N=mg/cosθ =mrw^2 ?
Thank you
Attachments
Last edited: