SUMMARY
The equation 2(sin(a)cos(a)) = sin(2a) is proven using the sine addition formula, sin(a + b) = sin(a)cos(b) + cos(a)sin(b). By setting b equal to a, the identity simplifies to sin(2a). The discussion also highlights the use of Euler's identity, exp(iθ) = cos(θ) + i sin(θ), to derive trigonometric identities. Various proofs, including geometric interpretations and complex exponential forms, are presented, demonstrating the versatility of these mathematical concepts.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of trigonometric identities, specifically the sine addition formula.
- Familiarity with Euler's identity and complex numbers.
- Basic knowledge of geometric interpretations of trigonometric functions.
- Ability to manipulate algebraic expressions involving trigonometric functions.
NEXT STEPS
- Study the derivation of the sine addition formula in detail.
- Learn about complex numbers and their applications in trigonometry.
- Explore geometric proofs of trigonometric identities.
- Investigate other trigonometric identities and their proofs using Euler's formula.
USEFUL FOR
Students of mathematics, educators teaching trigonometry, and anyone interested in deepening their understanding of trigonometric identities and their proofs.
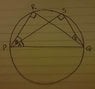
 would have been a lot better if i'd started off with a circle
would have been a lot better if i'd started off with a circle