mjmadraswala
- 1
- 0
- TL;DR
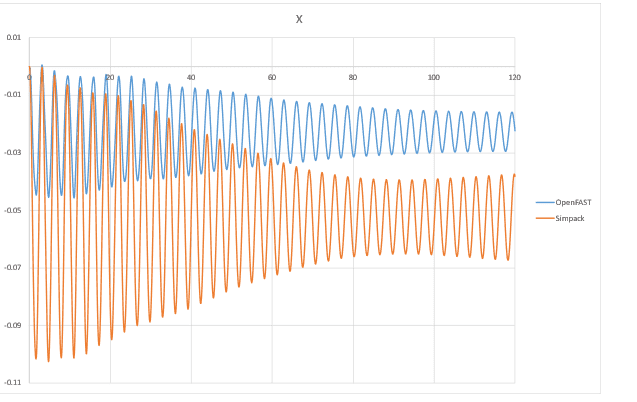
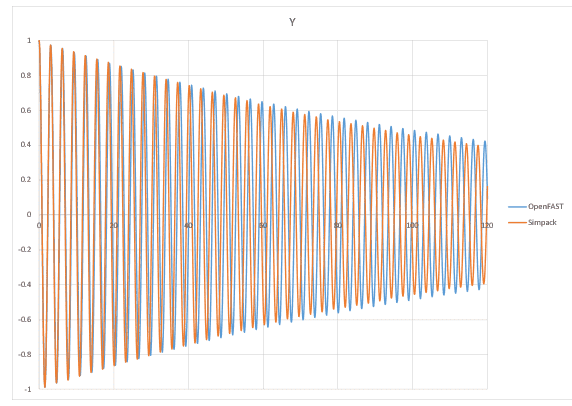
- I have been conducting free decay analysis on the 5-MW-wind turbine model provided by SIMPACK . I wanted to compare the free decay results with OPENFAST simulation. Hence, I applied a initial displacement of 1m on the tower top in the Y direction. While comparing the results with OPENFAST the decay seems to match in the Y direction but the decay along X-direction seems to vary in magnitude(see snapshot below). SIMPACK has a higher magnitude of decay which could be due to the offset in C.M of the
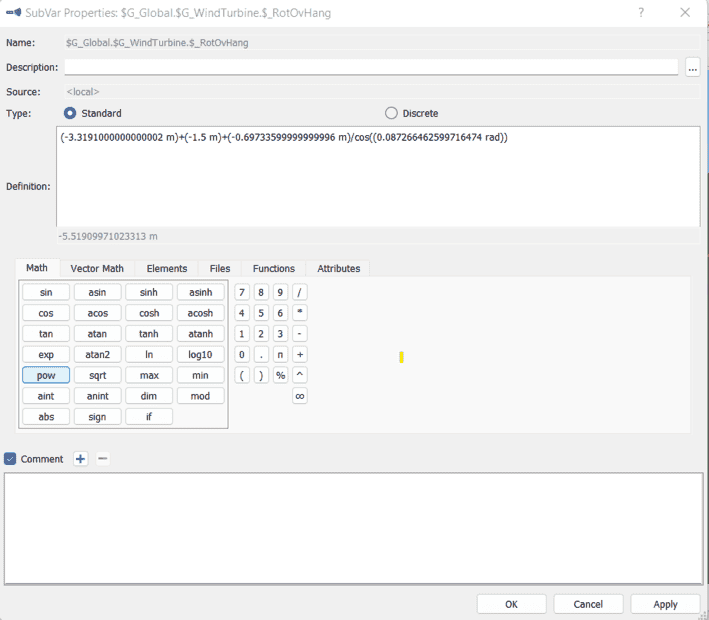
I have been conducting free decay analysis on the NREL 5-MW-wind turbine model provided by SIMPACK . I wanted to compare the free decay results with OPENFAST simulation. Hence, I applied a initial displacement of 1m on the tower top in the Y direction. While comparing the results with OPENFAST the decay seems to match in the Y direction but the decay along X-direction seems to vary in magnitude(see snapshot below). SIMPACK has a higher magnitude of decay which could be due to the offset in C.M of the nacelle or the Hub. I also found out that there is an offset in the overhang length between SIMPACK and OPENFAST, but as per the structural parameters of the NREL 5 MW the C.M of the nacelle and the hub seems to be at the correct co-ordinates on SIMPACK. I checked manually the distance of the center of hub to the tower axis, which is different from the OvrHang length defined in the model(check snapshot)
If anyone has worked with the same model on SIMPACK explain what do the values represent in the subvar RotOvrHang on SIMPACK?
Appreciate your help on this matter.
If anyone has worked with the same model on SIMPACK explain what do the values represent in the subvar RotOvrHang on SIMPACK?
Appreciate your help on this matter.