guyvsdcsniper
- 264
- 37
- Homework Statement
- Find the work per particle required to assemble such a configuration.
Problem
- Relevant Equations
- W=qV
The problem states to find the work per particle to assemble the following NaCl chain.
I just want to post my work here to verify I have the correct answer.
My work is attached in the image provided.
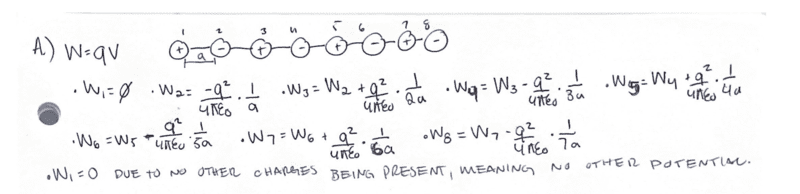
I just want to post my work here to verify I have the correct answer.
My work is attached in the image provided.